What’s the Process of Successful Well Intervention
Well intervention holds a pivotal position within the oil and gas sector, facilitating the enhancement of production by optimizing and maintaining oil wells. A comprehensive grasp of the nuanced well intervention process is imperative to guarantee the success and sustained efficiency of operations in the oil and gas industry. This article delves into the essential facets of well intervention, covering its foundational principles to the cutting-edge technological developments that are currently influencing the industry.

Understanding Well Intervention
Well intervention refers to a set of activities and techniques carried out on oil or gas wells to enhance or restore their performance. The primary goal of well intervention is to optimize the production of hydrocarbons from the subsurface reservoirs. This process becomes necessary when wells face challenges such as reduced flow rates, mechanical issues, or other factors affecting their efficiency.
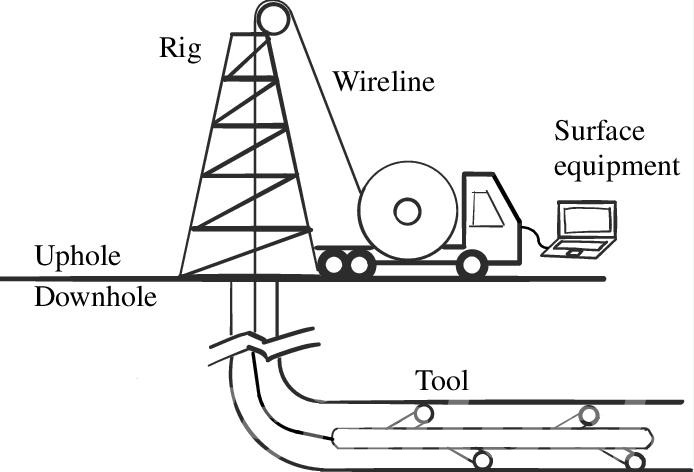
Well intervention can take various forms, including mechanical, hydraulic, or chemical methods, depending on the specific issues encountered. Here are some common types of well intervention:
- Mechanical Interventions: This involves using tools or equipment to physically address issues within the well. It may include tasks such as cleaning out debris, removing scale or deposits, or repairing damaged components.
- Hydraulic Interventions: Hydraulic interventions use fluids to address well issues. For example, hydraulic fracturing involves injecting fluids into the reservoir to enhance the flow of hydrocarbons.
- Chemical Interventions: Chemical treatments may be applied to the well to address issues like scale formation or corrosion. These treatments aim to improve the well’s productivity by eliminating or mitigating detrimental substances.
The well intervention process typically involves careful planning, risk assessment, and the deployment of specialized tools and equipment. Before intervention, a thorough analysis of well data, reservoir conditions, and historical performance is conducted to make informed decisions.
Well intervention is a crucial aspect of well lifecycle management, contributing to maintaining or restoring well integrity, maximizing production rates, and extending the overall lifespan of oil and gas wells. It plays a vital role in ensuring the economic viability and efficiency of hydrocarbon extraction from subsurface reservoirs.
The Stages of Successful Well Intervention
While the previous outline provided a solid foundation, let’s dive deeper into each stage of a successful well intervention, exploring the intricacies and complexities involved.
1. Pre-Intervention Planning
- Defining Crystal-Clear Objectives: Beyond simply “boosting production,” delve into specifics. Aim to increase flow by a certain percentage, address a specific reservoir issue, or achieve enhanced data acquisition.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Don’t venture into the well blindly. Analyze production history, well logs, and geological models to understand the well’s health, potential challenges, and optimal intervention methods.
- Methodical Method Selection: Slickline for quick gauge runs, wireline for heavier perforating tools, or coiled tubing for complex stimulation jobs? Match the method to the objective and well characteristics.
- Risk Mitigation: Identify potential hazards like blowouts, equipment malfunction, or formation instability. Develop robust contingency plans and safety protocols to minimize risks.

- Equipping for Success: Choose the right tools for the job! From slickline units and logging tools to coiled tubing rigs and stimulation fluids, ensure equipment compatibility and optimal performance.
2. Intervention Execution
- Efficient Mobilization: Ensure the swift transportation of equipment and personnel to the well site. Prioritize rigorous safety protocols and meticulous setup procedures to establish a well-organized and secure operation.
- Mastery of Wellbore Access: Establish secure well control by utilizing blowout preventers and other safety measures. Navigate the wellbore with precision, ensuring a seamless entry and exit process for efficient operations.
- Downhole Precision: Execute tasks with precision by deploying tools with high accuracy. Whether running gauges, conducting perforations, stimulating reservoirs, or retrieving lost equipment, each task requires expertise and meticulous execution.
- Real-Time Vigilance: Maintain continuous vigilance by monitoring data feeds, pressure gauges, and operational parameters in real-time. Adapt procedures on the fly to ensure safety and optimize the effectiveness of the intervention. The ability to make real-time adjustments is crucial for a responsive and efficient operation.

3. Post-Intervention Evaluation
- Wellbore Cleanup: Eliminate any tools or debris remaining in the wellbore to ensure its readiness for production. Thorough cleaning serves as a preventive measure against potential complications in the future.
- Data Analysis: Scrutinize the data collected during and after the intervention. Evaluate the achievement of objectives, pinpoint areas for enhancement, and gather valuable insights to inform future operations. Data analysis is integral to informed decision-making.
- Equipment Demobilization: Dismantle and remove equipment from the well site in a secure manner, restoring the environment to its original state. A systematic demobilization process showcases responsible stewardship and environmental consideration.
- Knowledge Documentation: Chronicle the entire intervention process, documenting successes, challenges, and unforeseen outcomes. This recorded knowledge becomes a foundation for shared insights, fostering continuous improvement in subsequent interventions. The lessons learned contribute to the evolution of best practices in the industry.
Technological Advancements in Well Intervention
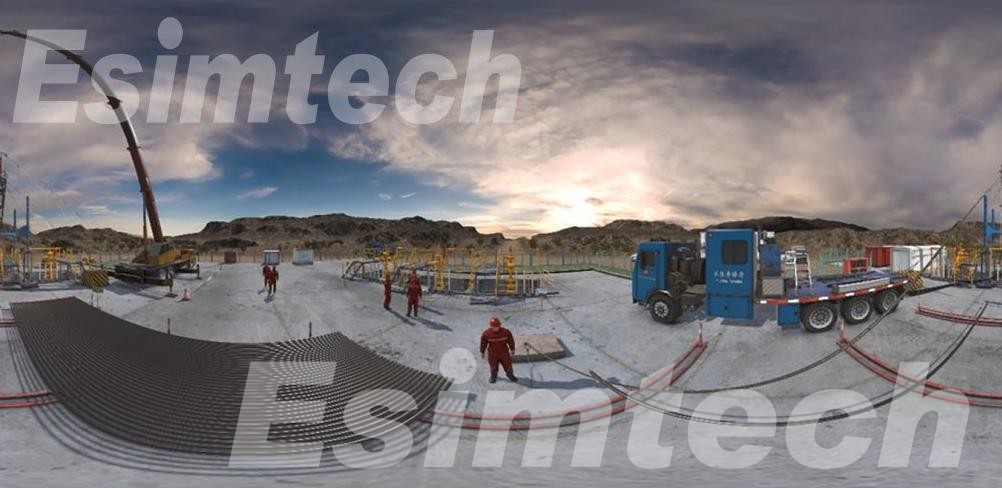
Well intervention simulation technology within the oil and gas industry are specialized software programs or physical models meticulously crafted to replicate a diverse range of well intervention operations. These operations span across the drilling, completion, and production phases of a well’s lifecycle. The primary purpose of these simulators is to furnish a realistic and secure environment for training, strategic planning, and the enhancement of well intervention activities.
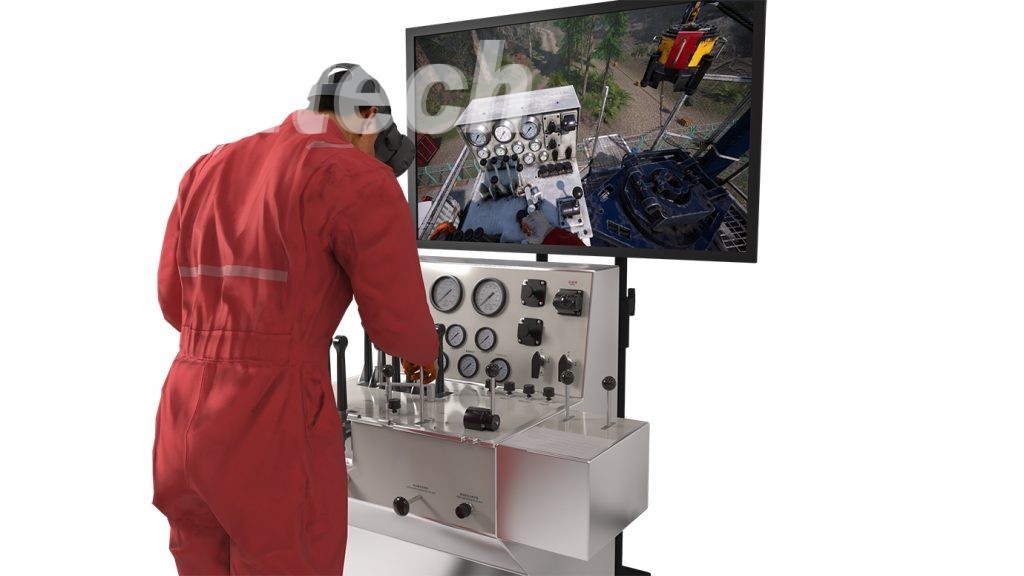

These simulators are adept at replicating various well intervention operations, including wireline, coiled tubing, hydraulic workover, snubbing, and fishing operations. Their capabilities extend to mimicking the behavior of a well and its adjacent formation under diverse operational scenarios. These scenarios encompass fluctuations in well pressure and temperature, alterations in wellbore geometry, and modifications in reservoir properties. Additionally, the simulators can accurately reproduce the responses of different intervention tools and equipment, such as pumps, valves, and sensors. This enables operators to practice the precise operation and placement of these tools within a controlled and secure environment.

The utilization of well intervention simulators carries several benefits. Firstly, it plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of accidents by allowing operators to hone their skills in a risk-free setting. Secondly, these simulators contribute to heightened operational efficiency by providing a platform for operators to refine their techniques and strategies. Furthermore, the simulators facilitate the improvement of the overall quality of well intervention operations throughout the entire lifecycle of the well. They empower operators to identify potential issues and assess diverse intervention strategies before their implementation in real-world field scenarios.
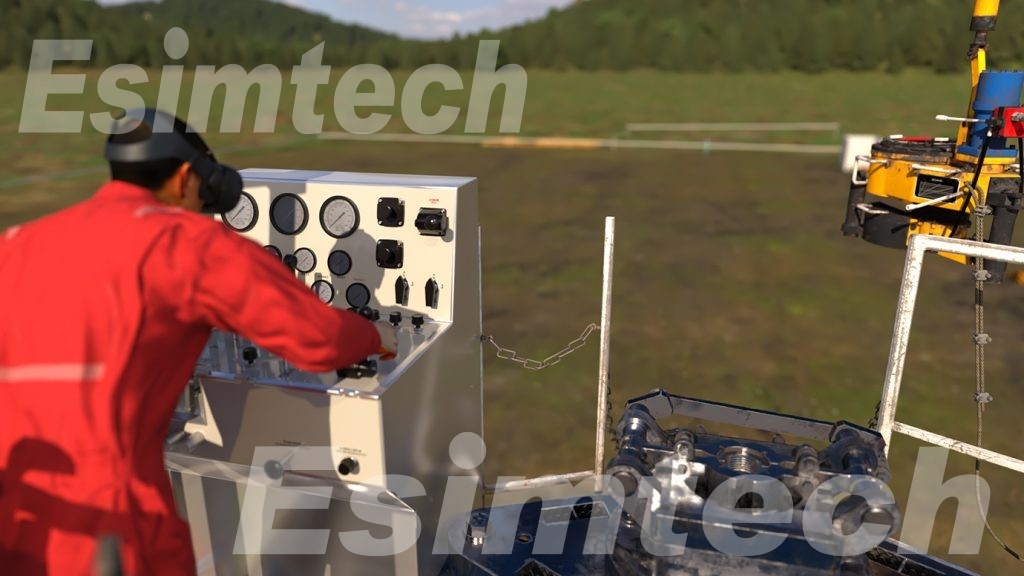

In essence, the incorporation of well intervention simulators yields a multitude of advantages for the oil and gas industry. Not only do they contribute to time and cost savings, but they also elevate the safety and efficiency of operations. By leveraging these simulators, the industry can proactively address challenges, refine interventions, and ensure the optimal performance of well interventions, ultimately enhancing the sustainability and success of oil and gas operations.
Conclusion
In summary, well intervention is a crucial process in the oil and gas industry, optimizing production and maintaining well efficiency. We explored the fundamental principles and cutting-edge technologies shaping well intervention. The stages of success were detailed, emphasizing clear objectives, data-driven decisions, meticulous planning, and post-intervention evaluation. Technological advancements, like well intervention simulators, offer secure training environments, enhancing safety and efficiency. Successful well intervention ensures well integrity, maximizes production, and extends the lifespan of oil and gas wells, contributing to the industry’s sustainability and success.

