What are Horizontal Wells: Significance, Techniques and the Vital Role of Simulation
Horizontal wells have emerged as a game changer in the hydrocarbon production industry. Horizontal wells, also known as “snake wells,” represent a revolutionary approach to drilling that offers numerous advantages over traditional vertical wells. In this article, we will delve into the world of horizontal wells, investigating their significance, techniques, and profound impact on the energy sector.|
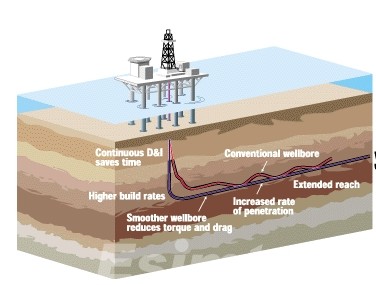
Understanding Horizontal Wells
Horizontal wells, as the name implies, deviate from the traditional vertical drilling method. Horizontal wells, as opposed to drilling straight down into the earth, take a curved path, extending horizontally beneath the surface through oil- or gas-bearing rock formations. This method of directional drilling allows access to previously untapped reservoirs.
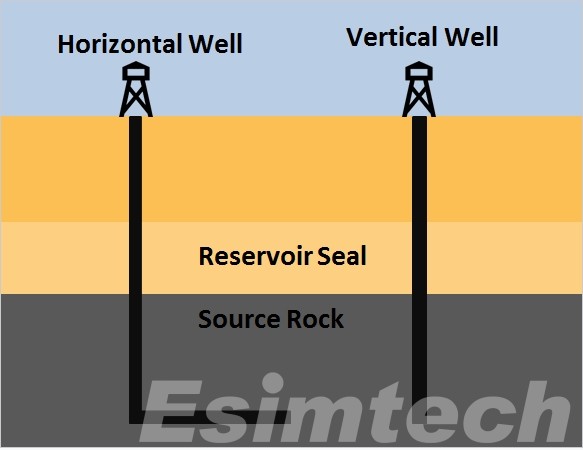
Techniques for Drilling Horizontal Wells
Directional Drilling
The fundamental drilling technique underlying horizontal wells is directional drilling. It begins as a standard vertical well, but at a certain depth, the drill bit is redirected horizontally. Specialized tools and measurements, such as a downhole drilling motor and measurement-while-drilling (MWD) systems, are used to guide the drill bit along the desired path.

Steering Tools
It is critical to maintain control over the wellbore’s direction. To ensure precise well steering, tools such as rotary steerable systems and mud motors are used.
Casing and Cementing
To maintain structural integrity and prevent fluid migration between geological layers, horizontal wells require additional casing and cementing at the curve and horizontal sections.
Perforation and Completion
Following completion of drilling, the wellbore is perforated to allow hydrocarbons to flow into the well. Completion operations, like hydraulic fracturing, may be performed to stimulate reservoir production.
Production Logging
Continuous monitoring and production logging are essential for horizontal wells. These operations help assess reservoir performance, identify issues, and optimize production strategies.

The Significance of Horizontal Wells
Horizontal wells have significantly transformed the oil and gas industry.
Enhanced Recovery Rates
Horizontal well drilling allows access to a larger portion of the reservoir, increasing hydrocarbon extraction significantly. When compared to vertical wells, this results in higher recovery rates.
Economic Efficiency
Horizontal wells’ financial benefits frequently outweigh their initial drilling costs, making them a wise investment for operators.
Environmental Responsibility
Reduced surface disturbance and environmental impact aid in more responsible resource extraction.
Reservoir Management
Horizontal drilling improves reservoir management, extending the life of oil fields and increasing production.
Maximizing Resources
As the global demand for energy grows, horizontal wells become increasingly important in maximizing oil and gas resources.
Mitigated Water and Gas Coning
Horizontal wells are less susceptible to water and gas coning, which is a common problem in vertical wells. As a result, the hydrocarbon product is less diluted and the crude oil is of higher quality.

The Role of Simulation in Enhancing Horizontal Wells
The Importance of Simulation in Horizontal Wells
The precision required for horizontal oil drilling demands careful planning, training, and continuous monitoring. This is where simulation technology proves invaluable.

1. Training and Skill Development
Horizontal drilling requires a specific skill set. Drillers need to be well-versed in directional drilling, downhole tool management, and geosteering. Drilling an well control training simulation technology provides a risk-free environment for training and skill development, allowing drillers to practice and refine their techniques.
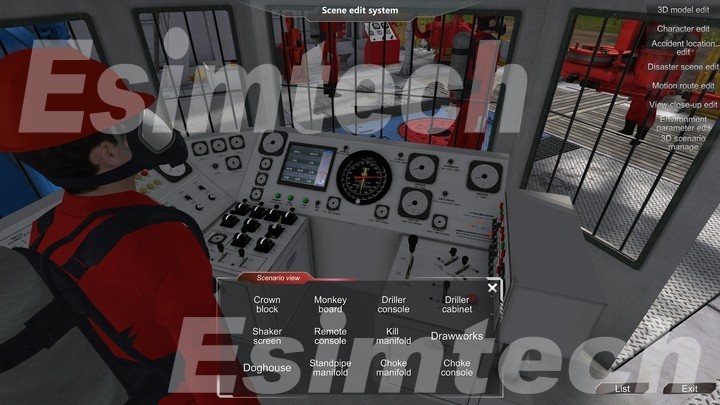
2. Risk Mitigation
Horizontal drilling projects come with significant financial and environmental risks. Simulations enable operators to rehearse drilling procedures, anticipate potential challenges, and develop contingency plans. This practice minimizes risks without the associated costs and dangers of real-world drilling.
3. Equipment Familiarization
Operators can use downhole simulation tools to become acquainted with specialized equipment used in horizontal drilling, such as downhole drilling motors, measurement-while-drilling (MWD) systems, and rotary steerable systems. This familiarity is essential for smooth drilling operations.
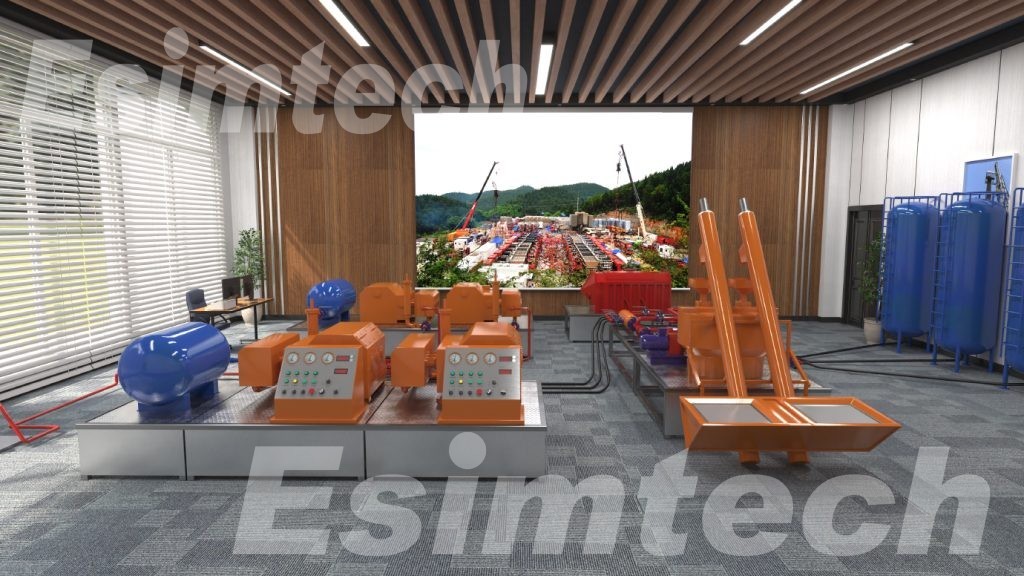

4. Operational Optimization
Simulations allow operators to test various drilling strategies, assess their impact on the reservoir, and refine their approaches. This process optimizes drilling parameters, minimizes downtime, and enhances drilling efficiency.
5. Emergency Response Drills
In the event of unexpected challenges during drilling, operators must be prepared to respond swiftly and effectively. Emergency simulation systems help drillers practice emergency procedures, ensuring they are well-prepared to manage unforeseen situations.

Key Components of Simulation in Horizontal Drilling
- Virtual Well Environments
Simulations create realistic well environments where operators can practice drilling, make adjustments, and address potential challenges in a controlled setting. These virtual scenarios can replicate various geological formations and conditions, allowing drillers to adapt to different challenges.
- Interactive Drilling Software
Drilling simulators offer interactive software that enables operators to make real-time decisions and witness the consequences of those decisions in a virtual environment. These simulators provide valuable feedback and insights.

- Reservoir Modeling
Advanced simulation tools can incorporate reservoir data and modeling to accurately represent geological conditions. This allows for precise geosteering and reservoir management, contributing to enhanced recovery rates.
- Data Visualization
Oil and gas simulation software provides detailed data visualization, including information about drilling parameters, wellbore conditions, and downhole measurements. This helps operators make informed decisions and monitor drilling operations effectively.
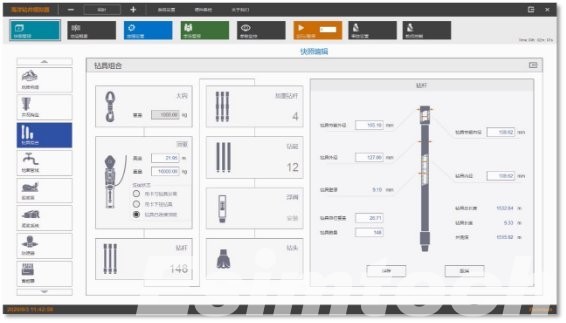
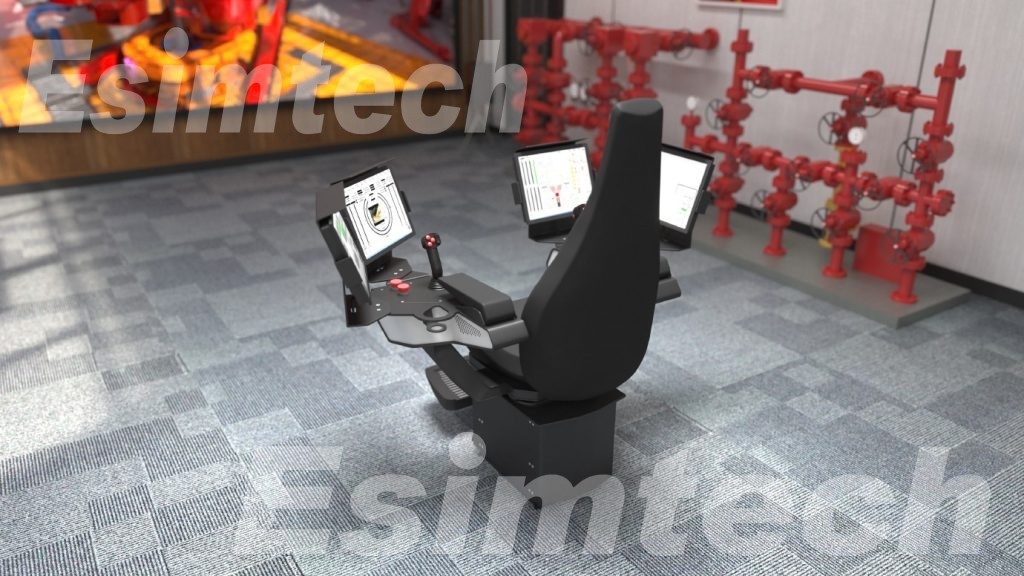
- Drilling Equipment Integration
Drilling simulators can work in tandem with drilling equipment to simulate the use of specialized tools and equipment. This allows operators to practice using the actual tools they will encounter while drilling in the field.

Conclusion
Horizontal wells are a ground-breaking approach to resource extraction, providing a variety of benefits that have a significant impact on the oil and gas industry. They play an important role in meeting the world’s energy demands while also ensuring a sustainable and efficient approach to resource extraction. Simulation technology contributes to the success of horizontal well drilling projects by providing a safe and efficient means of preparing for drilling operations, thereby improving safety, efficiency, and overall productivity in the oil and gas industry.
