Well Stimulation Techniques: Cost vs. Benefit Analysis
In the oil and gas industry, well stimulation techniques are used to increase the amount of oil or gas that can be extracted from underground reservoirs. These methods, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and acidizing, help make the rocks more permeable so that the oil or gas flows more easily. To decide whether to use these techniques, it’s important to weigh their costs against the benefits they bring.
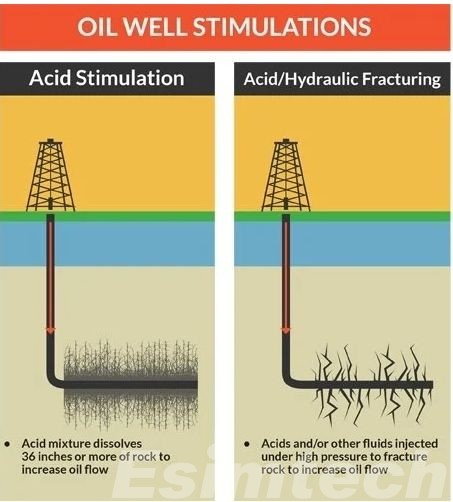
Cost Breakdown of Well Stimulation Techniques
The cost of well stimulation varies significantly depending on the chosen method and well characteristics. Here I use a sheet to summarize the cost breakdown of different well stimulation techniques.
| Technique | Cost Factors | Description |
| Hydraulic Fracturing | Fluids | Cost of water, chemicals, and proppant based on volume and type required for well depth and formation. |
| Equipment | High-pressure pumps, fracturing trucks, downhole injection equipment – cost depends on complexity (number of fracturing stages). | |
| Labor | Skilled professionals to operate equipment and oversee the process. | |
| Logistics | Mobilization of equipment and personnel to the well site. | |
| Acid Fracturing | Acid Type | Cost varies depending on the specific acid used to address formation damage (stronger acids typically more expensive). |
| Volume | Amount of acid required is determined by severity of damage and well size (larger wells with more damage require more acid). | |
| Equipment and Labor | Mobilization of equipment and personnel for acid fracturing. | |
| Matrix Acidizing | Acid Selection | Similar to acid fracturing, cost depends on the chosen acid type. |
| Volume and Delivery Method | Cost depends on amount of acid and method used for downhole delivery (coiled tubing vs. pumping). | |
| Operational Costs | Equipment and personnel mobilization, but less extensive compared to other techniques. | |
| Solvent or Surfactant Treatments | Treatment Type | Specific solvent/surfactant used depends on blockage type, impacting cost. |
| Volume and Delivery | Amount of solution needed and downhole injection method affect the overall cost. | |
| Operational Footprint | Simpler techniques minimize equipment and personnel needs, leading to lower operational costs. |
Benefit Analysis of Well Stimulation Techniques
We’ve explored the costs involved in well stimulation techniques, but the real question is: what kind of payback can you expect? Here’s a closer look at the benefits these techniques offer:
- Enhanced Permeability: The channels through which oil and natural gas pass through rock formations are very complex. Well drilling and other processes can damage these pathways, reducing permeability, or how easily fluids can flow. Stimulation techniques like fracking and acid treatments act like bulldozers, clearing blockages and creating new pathways. This improved permeability allows oil and gas to move more freely towards the wellbore, significantly increasing production rates.

- Unlocking Tight Reservoirs: In some areas, the rock formations are naturally very dense and have extremely low permeability. Without stimulation, these “tight reservoirs” wouldn’t be commercially viable. Techniques like fracking are essential for creating fractures and increasing permeability in these formations, making it possible to extract oil and gas at economic rates.
- Extending Well Life: Over time, natural formations near the wellbore can become damaged, restricting flow. Stimulation techniques can help restore or even improve permeability around the wellbore. This can breathe new life into a well that might otherwise be nearing the end of its productive lifespan. By keeping the flow efficient, stimulation can help a well produce for a longer period, maximizing the overall recovery of oil and gas from the reservoir.
- Targeted Treatments: Not all wellbore challenges require a one-size-fits-all approach. Matrix acidizing, for example, allows for a more focused treatment by injecting acid directly into the rock formation. This targeted approach can address specific damage deep within the rock, improving flow without extensive fracturing.
While the primary benefit of well stimulation is increased production, there are additional advantages to consider:
- Stimulation techniques can provide valuable data about the reservoir’s characteristics, such as permeability and formation pressure. This information helps operators make informed decisions about future production strategies and optimize reservoir management.
- By maximizing recovery from existing wells, stimulation techniques can help reduce the need for drilling new wells, potentially lowering the environmental footprint of oil and gas production.

It’s important to remember that the effectiveness of any stimulation technique will depend on the specific well and reservoir characteristics. A thorough evaluation is crucial to determine the optimal approach and maximize the potential benefits of well stimulation.
Cost vs. Benefit Comparison
Evaluating the cost versus benefit of well-stimulation techniques involves a comprehensive analysis of both the investment required and the incremental production achieved. Here’s a deeper dive into some key factors to consider:
1. Expected Production Increase vs. Stimulation Cost: This is the core consideration. The additional oil or gas produced from the well over its lifespan needs to generate enough revenue to cover the stimulation cost and yield a profitable return. Operators should utilize reservoir modeling and historical data to create accurate production forecasts that factor in the impact of stimulation.
2. Reservoir Characteristics
The effectiveness and economic viability of stimulation techniques heavily depend on the characteristics of the targeted formation. Here’s a breakdown:
Permeability: Formations with low permeability, like shale gas reservoirs, often require stimulation to achieve economic production rates. In such cases, the cost of stimulation can be justified by the significant production increase it enables.
Formation Damage: Damage caused by drilling fluids or the natural formation itself can restrict oil and gas flow. Stimulation techniques can effectively remove this damage, leading to a substantial production boost that justifies the cost.
Presence of Natural Fractures: Some formations possess natural fractures that can enhance flow. In such cases, the benefit of stimulation may be lower, and a cost-benefit analysis should determine if the production increase outweighs the stimulation cost.
3. Well Economics: The overall economic health of the well needs to be factored in. This includes:
Operational Costs: Ongoing costs associated with well operation and maintenance should be considered. Stimulation can sometimes reduce these costs by extending the well’s productive life and delaying the need for workovers.
Oil and Gas Prices: Fluctuations in oil and gas prices directly impact the revenue generated from increased production. When prices are high, the benefit of stimulation is amplified, making it a more attractive option.

4. Long-Term Considerations: Well stimulation is an investment, and the benefits extend beyond immediate production increases. Stimulation can help:
Extend Well Life: By improving wellbore health and preventing formation damage, stimulation can extend the period of economic production from a well, maximizing recoverable reserves.
Reduce Environmental Impact: Stimulation can help revitalize existing wells, potentially reducing the need to drill new wells, which can have a smaller environmental footprint.
Conclusion
By weighing these cost and benefit factors, operators can make wise decisions about adopting well stimulation technology. Another point to note is that the optimal method may vary depending on the specific well and reservoir characteristics. Therefore, consulting experienced engineers and utilizing advanced economic modeling tools can significantly improve the accuracy of cost-benefit analysis and ultimately make the right investment decisions.
