ESIM-FLS2 Compound Logging Simulator
- Preciseness
- Precise mathematical and physical model
- Reliability
- Stable and reliable software and hardware
- Service
- Timely and considerate after-sale service
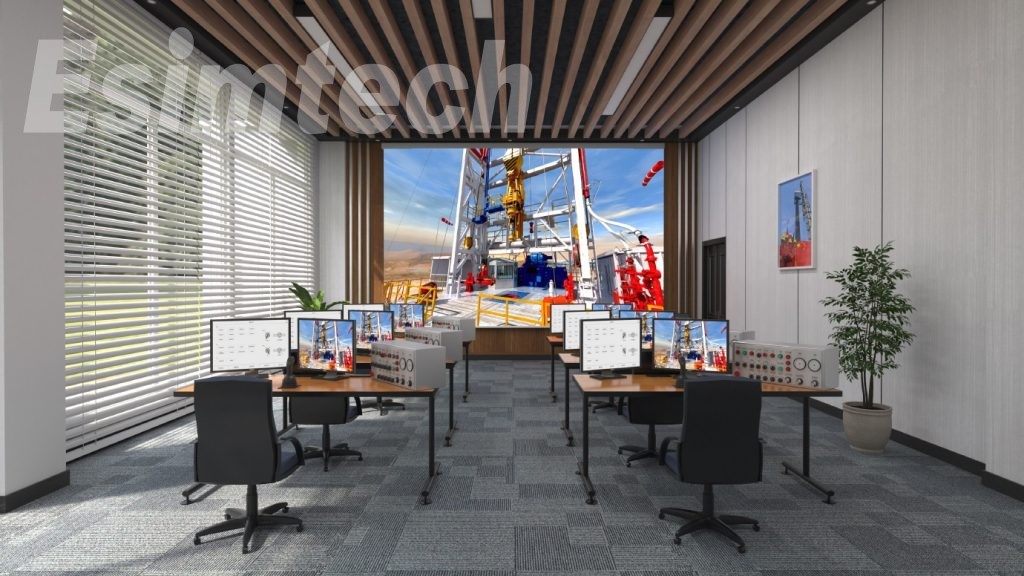
ESIM-FLS2 compound logging simulation training system is an advanced simulation training system used to provide training to operators, logging crew in training centers as well as petroleum colleges.
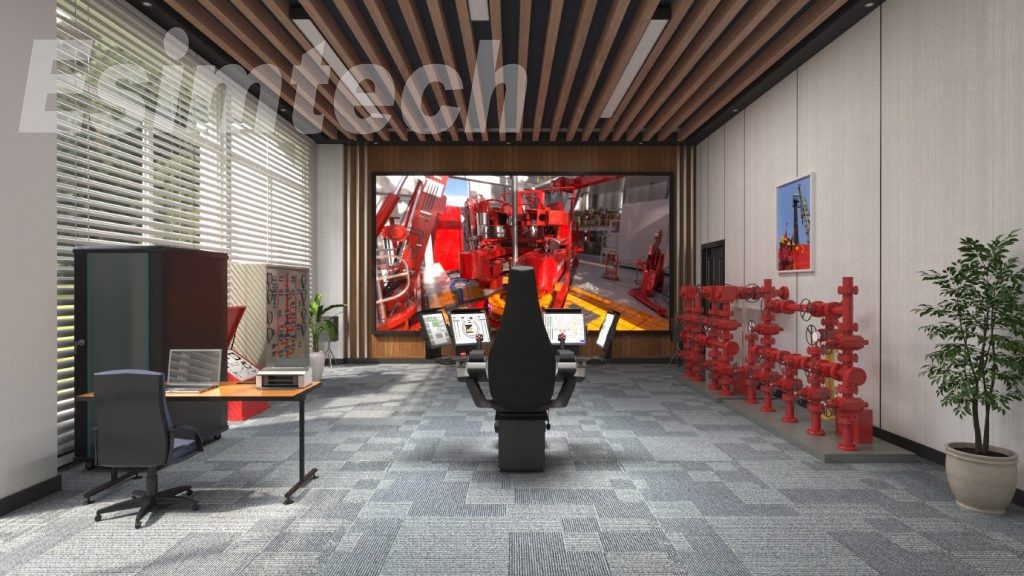
The system adopts a full-size logging equipment room, sand table well site model, sensor models, advanced logging software, drilling accidents modeling software and sensor detecting software designed in our own company. It presents the whole process of compound logging. Through the training of this system, students can master various operation skills and experience in treating drilling accidents.
System Features
- Presenting well site constitute and the role logging plays in drilling
- Training students constitute and operation of gas detecting system
- Simulating 46 kinds of accidents in the drilling process
- Training students to master the role sensors play in logging
- Presenting how to operate various software through KVM
1. Introduction
The compound logging simulation training system is an advanced training simulation system, used to provide compound logging training for the logging crew, logging workers in training centers as well as petroleum universities and colleges. The system adopts a full-size logging unit, sand table of well site model, sensor models, advanced logging software, as well as the drilling accidents simulation software and sensor detection software developed by our company, providing trainings of the whole process of compound logging, and enabling students to master various operation skills and accident treating methods of compound logging.
System main functions:
-
Presenting well site constructions and the role logging plays in drilling operation;
-
Training students of the structure and operation methods of gas detection system;
-
Simulating 5 kinds, totally 46 items of accidents; Students can master various ways of accident forecast and treatment.
-
Familiarizing students the role sensors play in logging as well as the installation position of sensors in well site;
-
Instructor could demonstrate how to operate the software in the compound logging simulation training system through KVM system.
2. SystemComponent
2.1 Major Hardware
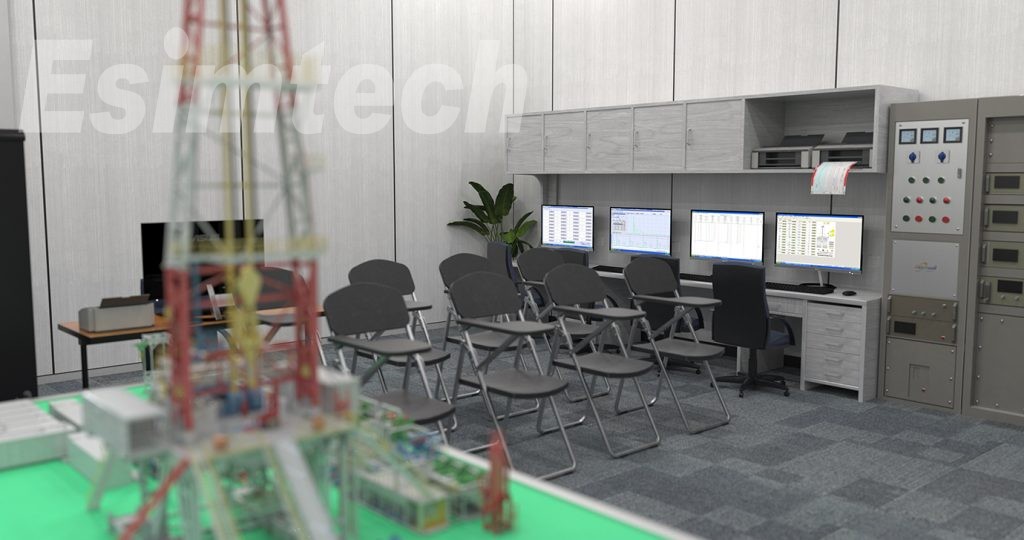
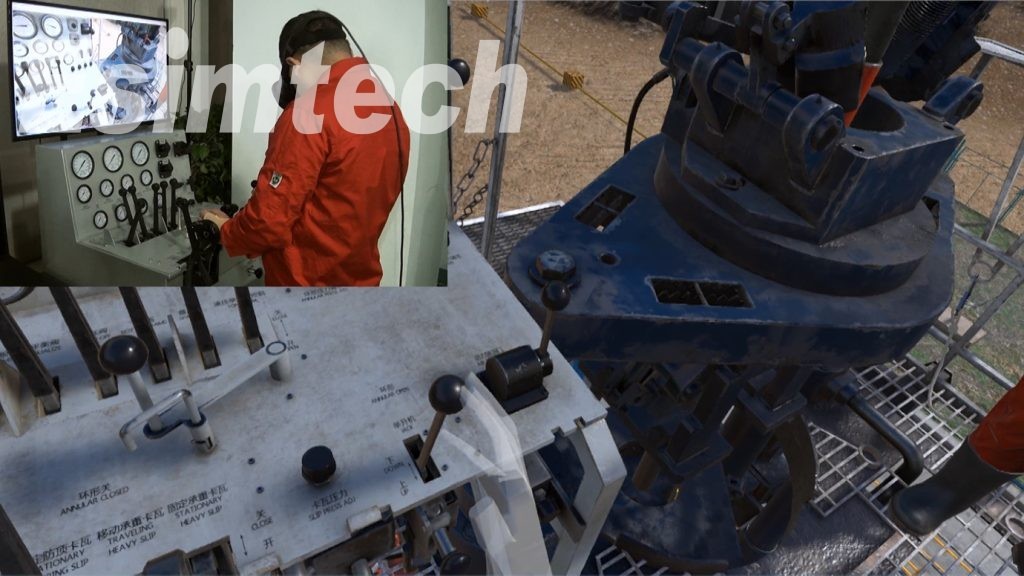
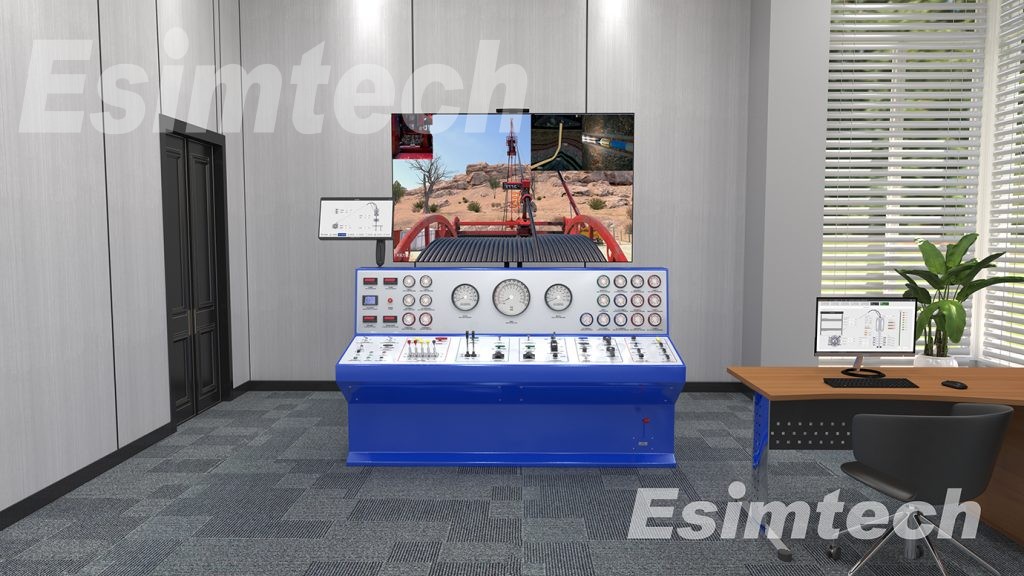
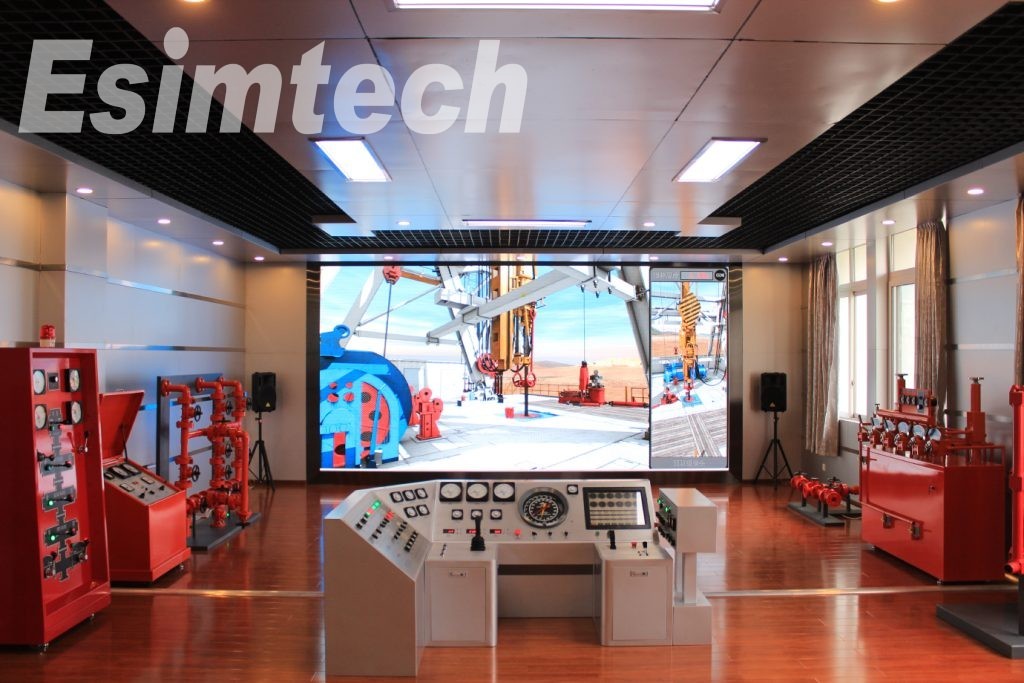
The structure of this system is as shown in figure 1. The system is composed of explosion-proof units, machine cabinet, gas detective device, sand table of well site model, sensor models, power controlling system, KVM system, projecting system, etc.
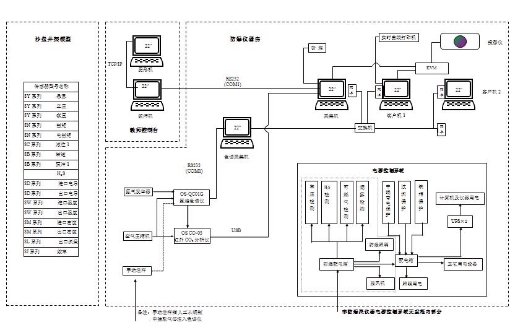
Figure 1 System hardware framework
-
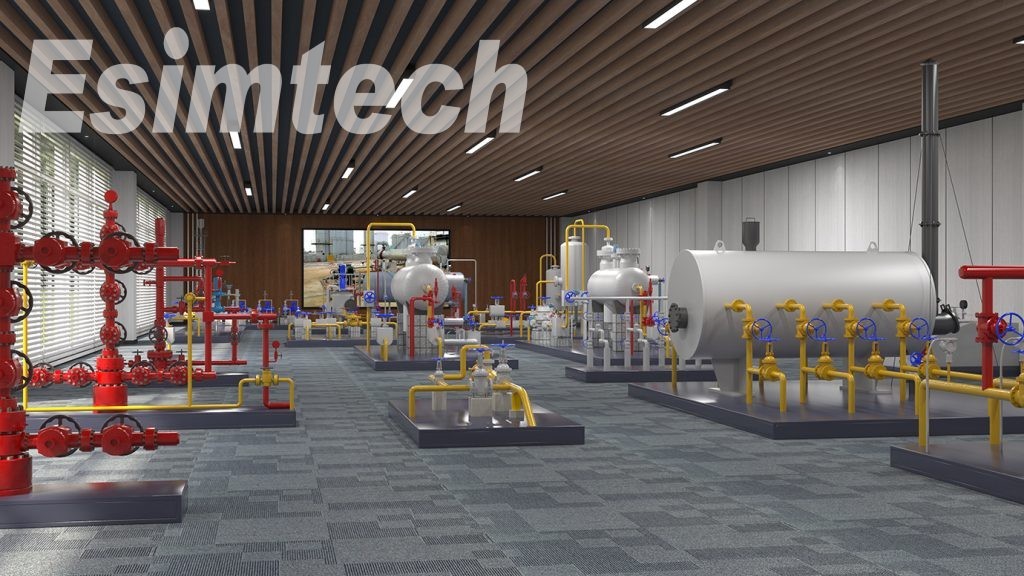
Explosive-proof units: Full size compound logging explosion-proof simulates the SK-2000FC logging units, the devices layout is the same as the real equipment is real site.
-
Machine cabinet: Machine cabinet integrates the computers, Hydrogen flame
-
Gas detection device: This device includes OS-QC01G hydrogen flame chromatograph, OS CO-03 infrared CO2 analyzer, hydrogen generator, air compressor and electrical mud degasser.
-
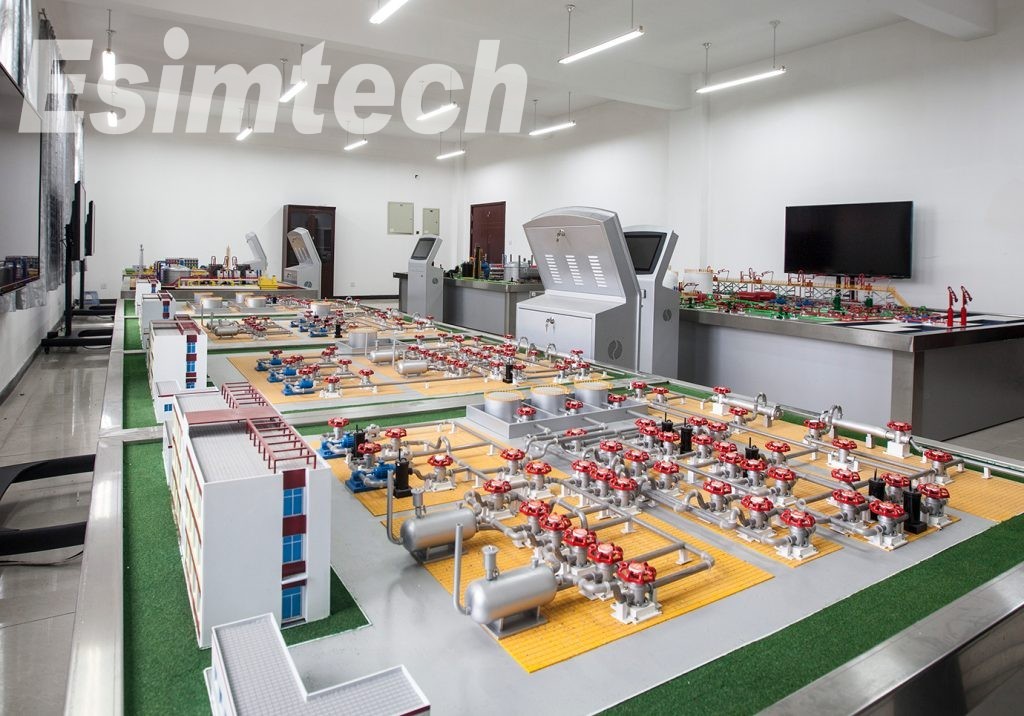
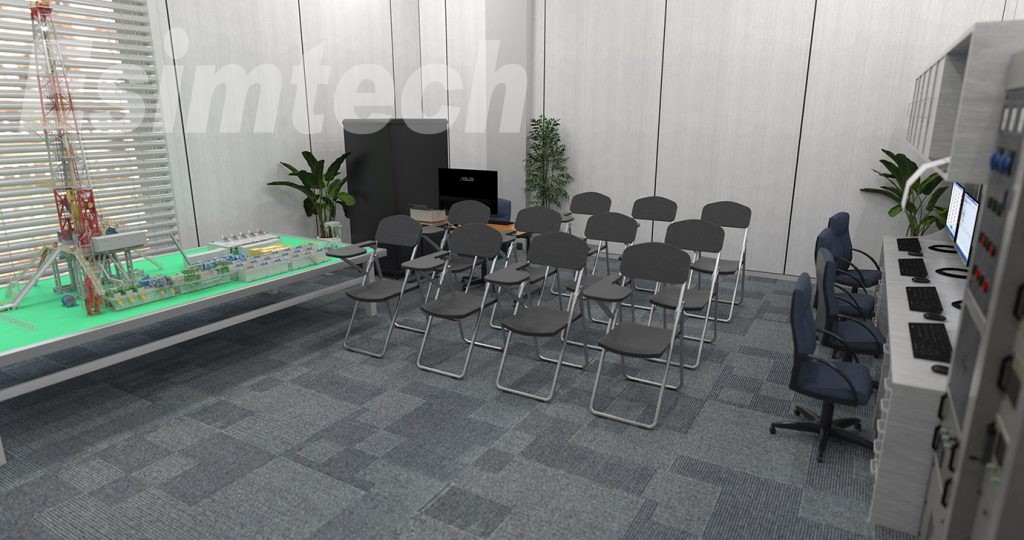
Sand table of well site model: the sand table model is made according to 70D drill rig by the scale of 1:20. The layout is exactly as the real well site, which makes up an impressive environment. Students can learn various systems of the rig, connection of various pipes, devices on rig floor, structure and functions of irrigation unit, etc.
-
Sensor models: The models include all sensors in real logging site, such as draw-works sensor, pump stroke sensor, rotary table rotation rate sensor, rotary table torque sensor, inflow/ outflow electric conductive sensor, inflow/ outflow density sensor, inflow/ outflow temperature sensor, ultra-sonic pit level sensor, electric torque sensor, standpipe pressure sensor, casing pressure sensor, hook load sensor, and H2S sensor
-
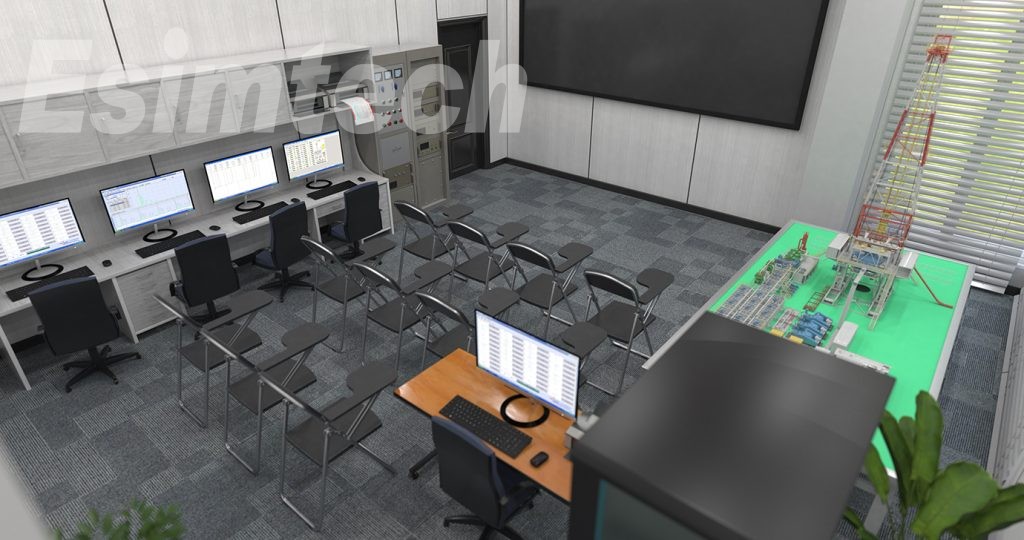
KVM system: KVM exchanging machine connects keyboard, mouse, VGA post. Instructor can visit and control the computers in logging units from one terminal, and demonstrate the student how to run the software, and can also choose to project any computer in logging unit on the screen. In this way, students can easily observe while learning.







2.2 System Software
-
Drilling accident simulation software
-
Compound logging software system
-
Sensor detection master control software
-
Sensor detection graphics software
-
Sensor detection PLC program
-
PowercontrolsystemPLC program
-
Sound effect control module software
-
System self-checking module
-
Students managing and automatic scoring software module
3.SystemFunctions
3.1 Functions and Features
-
The system provides an immersive logging environment. Gas detection system, explosion-proof system and compound logging software system adopt the devices from production site, which greatly improve the training quality.
-
Drilling accident simulation software, of which Esimtech Company owns independent intelligent property right, can simulate various accidents in drilling process, totally 6 kinds including 46 items of accidents. The software can playback the real logging data of 5 wells, and simulate drilling process such as tripping in, drilling, circulating, reaming, etc.
-
Logging software adopts the solution of Riglog developed by Shanghai Oushen Company. Riglog is the compound logging software extensively used in oilfield logging. It can acquire, record data of various sensors and chromatograph, and print the data at real time.
-
Sensor detection software system contains sensor detection master control software, sensor detection graphics software and sensor detection PLC program. When students don’t know where to install the sensor, they can insert it in the corresponding aviation connector, and the graphics program presents the data of the sensor such as the installing position and measurement range.
-
PLC program of power control system is mainly used in monitoring H2S sensor, flammable gas sensor, smog sensor and micro difference pressure sensor in logging units. When the sensors launch alarm, the electrical degasser will be powered off automatically.
-
The system can automatically score student’s operation. It can give score and point deducting reason automatically according to student’s operation procedure.
3.2 Simulated ProblemsandTroubles
-
Tripping in
1) Lost circulation when trippingout
2) Kick when trippingout
3) Influx when tripping out
4) Blowout when tripping out
5) Getting stuck when trippingout
6) Raisingandunfreezing
7) Oilorwater immersion when tripping in
8) Lost circulation when tripping in
9) Kick when tripping in
10) Influx when tripping in
11) Blowout when tripping in
12) Getting blocked when tripping in
13) Stuck pipe when tripping in
14) Drill pipe broken
15) Nozzle plugged
16) Abnormal standpipe pressure
-
Monitoring circulation and static state
1) Lost circulation
2) Oilorwater immersion
3) Influx
4) Kick
5) Blowout
-
Accidents when drilling and reaming
1) Bit service life end
2) Lost cone
3) Bit wornout
4) Drilling string leaking
5) Drilling string broken
6) Lost circulation
7) Well immersion (gas immersion, brine immersion)
8) Kick
9) Influx
10) Drill pipenotwell braked
12) Emptying
13) Nozzle plugged
14) Lost nozzle
15) Bit balledup
16) Stuck pipe
17) Wall collapse
18) Standpipe pressure changing becauseofdrilling fluid density
19) Pumpleaking
20) Pumpwater feeding failure
21) Bypass valvebroken
22) High pressure pipe leaking
-
H2S detection
1) Formation H2S
2) Non-formation H2S
-
Monitoring formation pressure
-
Damper failure
4. Technical Parameters andOperationalEnvironment
4.1 Technical Parameters
(1) Power supply: 110~220V/50~60Hz AC
(2) Power consumption: <6000W
(3) Resolution: 1024*768
(4) Brightness: >=4000ANSI Lumens
4.2 Operational Environment
(1) Area:>=10*8.5m
(2) Separate equipment power supply from light power supply
(3) Working temperature:0℃~30℃
(4) Relative humidity:<90%
5. SystemLayout and Program Interfaces

Figure 2 System whole layout
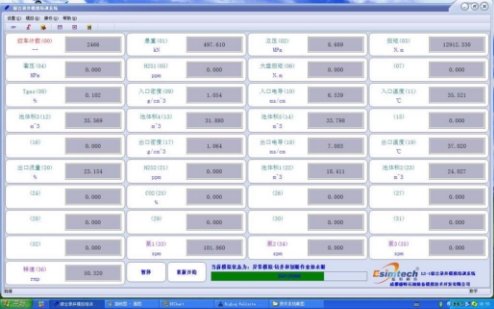
Figure 3 Drilling accident simulation software
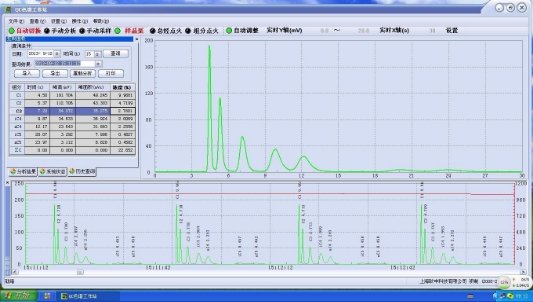
Figure 4 Chromatographic analysis interface
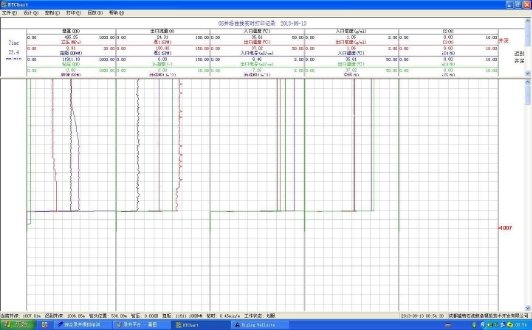
Figure 5 Real time curve interface
Figure 6 Logging platform software
Components


F&Q
- What is petroleum simulator?
A simulator is a device that simulates an environment for the purpose of training or research. A petroleum simulator is a set of devices that simulates the well site environment, the real operation devices, the operation method, parameter display way, etc. with which trainees can be access to a virtual well site environment, where they can get familiar with the relative devices, how to operate the devices, what phenomenon there will be if there is a problem, what’s happening underground, etc.
- Why is the simulator necessary to oil and gas industry?
Since the beginning of the 20th century, simulators have been used in different industries as tools to train and to facilitate the growth of the operators of the machinery. This type of training is, without a doubt, one of the most effective ways to mitigate labor risks, develop the skills needed, and increase productivity.
In oil and gas industry, accidents happen from time to time, such as blowout, H2S leakage, fire, explosion, machinery injuries, etc. Working in the oil and gas field is of high risk. According to statistics, almost 36% of these accidents were caused by mistakes in operation. Sufficient pre-post training is essential. A simulator makes this possible, which provides a virtual training environment, for new staff the get familiar with the working environment, site scene, and operation devices in advance. With the simulator, new staff can also experience the common incidents which may occur in real operations, and learn to judge and handle emergencies. So that in real work, most of the accidents can be judged or avoided in an early stage, and therefore reduces risks and increase production.
- What well control simulations does this well control simulator cover?
In well control operation, pressure control is very important. How the pressure is controlled? In the good control simulator, various scenes of kick can be simulated, both hard and soft shut-in procedures can be carried out. Meanwhile, various well-killing methods are provided, such as driller’s method, engineer’s method, volumetric method, bullheaded, low choke method, standpipe pressure method, etc.














