Vertical Drilling Used in the Oil and Gas Industry: What are Key Techniques and Why Choose Simulation Technology
Vertical drilling is the major method for reaching subsurface hydrocarbon resources in the oil and gas sector. This technique, sometimes known as “vertical well drilling,” involves boring a wellbore directly into the Earth’s crust, allowing access to lucrative oil and natural gas deposits. In this article, we will explore the principles, crucial techniques, applications of vertical drilling, and the significant role of simulation technology used in vertical well drilling.

The Principles of Vertical Drilling
Straight Downward Path
Vertical drilling, as the name implies, is all about building a wellbore that runs straight down into the ground, perpendicular to the surface. This is in contrast to directional drilling, which includes building wellbores that vary from a straight course in order to reach certain targets.
Drilling Rig
A drilling rig, a complicated piece of machinery designed to bore through many types of subterranean materials, is required for vertical drilling. The drilling rig is equipped with a drilling bit, drill pipe, and other essential tools to facilitate the drilling process.

Mud Circulation
A specialized drilling fluid, known as “mud,” is poured down the drill pipe and into the wellbore during drilling. The mud serves several functions, including cooling and lubricating the drill bit, stabilizing the wellbore, and transporting cuttings (rock and soil particles) to the surface for analysis.

Key Techniques Used in Vertical Drilling
Spudding
Spudding is a common first step in the drilling process. This entails utilizing a specialized spud bit to drill a shallow starting hole or “spud” at the surface. This first hole ensures the stability of subsequent drilling operations.
Rotary Drilling
Rotary drilling is the most frequent and widely utilized vertical drilling technology. A spinning drill bit linked to a drill pipe is used. The bit cuts into the subsurface material, and the cuttings are brought to the surface using a circulating drilling fluid (often called “drilling mud”). This method is effective in drilling through various geological formations.
Percussion Drilling
Percussion drilling, also known as cable tool drilling, involves repeatedly raising and dropping a heavy chisel-like bit to break up rock formations. This method is less prevalent today, but it is still employed in select cases, such as drilling through hard rock.
Air Rotary Drilling
In air rotary drilling, compressed air is used to remove cuttings and cool the drill bit. This method is particularly useful in drilling through unconsolidated or loosely consolidated formations, such as sands and gravels.
Coring
A cylindrical core sample is taken from the subsurface during core drilling. This method is critical in mineral exploration, environmental assessment, and geotechnical studies for obtaining precise geological information. Both rotary and wireline coring systems can be used for core drilling.
Reverse Circulation Drilling
Reverse circulation drilling is often used for obtaining large-diameter core samples in soft formations. In this technique, drilling fluid is pumped down the outer annulus of the drill pipe, carrying cuttings to the surface while the core sample is collected in the inner tube.
Auger Drilling
Auger drilling is appropriate for unconsolidated formations like dirt and sand. It entails using a helical auger bit to remove the material as it rotates and is pulled out of the hole. This method is commonly used for environmental and geotechnical investigations.
Diamond Drilling
Diamond drilling uses a specialized diamond-tipped bit to create a core sample. It is highly precise and suitable for hard rock formations. This method is widely used in mineral exploration and geological research.
Direct Push Drilling
Direct push drilling is a minimal disturbance technique used in environmental and geotechnical applications. It involves pushing a toolstring into the ground to collect soil and groundwater samples without removing soil cuttings.
Geothermal Drilling
Geothermal drilling techniques are employed to access underground geothermal reservoirs. These systems are designed to drill to significant depths and tap into the Earth’s natural heat for energy production.
Each of these vertical drilling techniques is selected based on the geological characteristics of the subsurface, the specific drilling objectives, and the type of materials that need to be penetrated.

Applications of Vertical Drilling in the Oil and Gas Industry
Exploration and Production
Vertical drilling is frequently the first step in the exploration and production of oil and gas. Vertical wells are dug to reach deep subterranean hydrocarbon sources. Once in place, the well can operate as a conduit for the extraction of these important resources.
Reservoir Characterization
Vertical drilling is crucial for determining the characteristics of oil and gas reserves. Geologists can acquire insights into the composition, porosity, and permeability of the subsurface strata by evaluating the geological formations found while drilling, which aids in determining the reservoir’s prospective production.
Workover Operations
Vertical drilling is utilized in well workover operations, which are intended to maintain, repair, or improve existing wells. By drilling a wellbore vertically into an existing well, operators can access different parts of the reservoir, isolate problem zones, or stimulate production.
Secondary and Tertiary Recovery
Vertical drilling is also employed in secondary and tertiary recovery methods, such as waterflooding and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques. By creating new wellbores or accessing existing ones, operators can introduce fluids into the reservoir to enhance hydrocarbon recovery.
Significant Role of Simulation Technology Used in Vertical Drilling
Oil and gas simulation technology is a powerful tool that replicates real-world scenarios in a virtual environment. In vertical drilling, it enables engineers and operators to model and visualize the drilling process before it occurs.
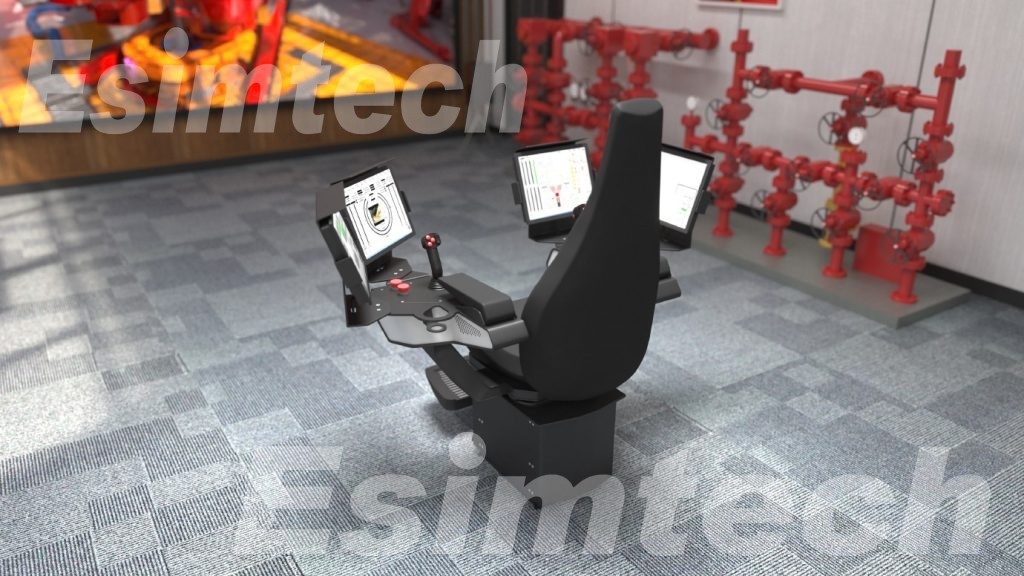

Advantages of Simulation Technology Used in Vertical Drilling
Risk Mitigation
One of the primary benefits of simulation technology to detect potential obstacles and dangers associated with drilling operations is one of its key benefits. Engineers can simulate various wellbore scenarios, identify potential concerns, and devise mitigation techniques. This preventive technique decreases the possibility of costly and time-consuming drilling setbacks.
Optimized Drilling Parameters
Drilling characteristics such as drilling fluid qualities, bit design, and equipment selection can all be fine-tuned using drilling simulation system. Engineers can use simulations to find the most effective drilling setups that maximize penetration rate while minimizing equipment wear and tear.
Training and Skill Development
Virtual drilling simulators are used for training purposes. They provide a safe and controlled environment for new drillers and engineers to develop their skills and gain hands-on experience before operating real drilling rigs. This reduces the learning curve and enhances overall safety.
Wellbore Stability Analysis
Simulation technology aids in determining wellbore stability, which is an important consideration in drilling. By modeling the wellbore’s geological conditions, drilling fluid properties, and mechanical parameters, engineers can predict potential instability issues and design solutions to prevent them.
Economic Feasibility
Simulations can assess the economic feasibility of drilling operations. By modeling different drilling scenarios, companies can make informed decisions on whether to proceed with drilling, evaluating factors such as projected costs, production potential, and the expected return on investment.

Applications of Simulation Technology in Vertical Drilling
Drilling Process Optimization
By selecting the best drilling fluid, modifying the bit design, and optimizing drilling parameters, simulations can improve the drilling process. This results in less drilling time, longer equipment life, and cost savings.
Well Placement
Well placement decisions are aided by well control simulators. Engineers can find the best well location for accessing hydrocarbon reserves by modeling the subsurface geology and reservoir parameters.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Simulations aid in the identification of safety hazards and the assessment of the environmental impact of drilling operations. This enables businesses to create comprehensive safety standards while reducing their environmental impact.
Training and Development
Drillers and engineers are trained using virtual drilling simulators. These drilling training simulation system ensure that people are properly trained to operate drilling equipment in an efficient and safe manner.
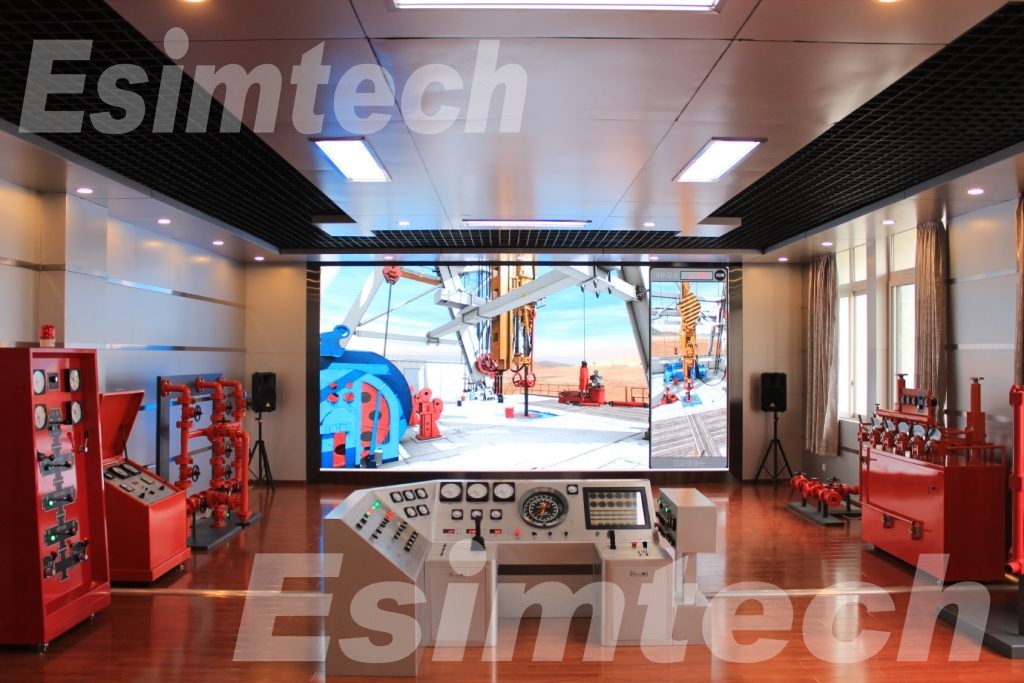

Reservoir Characterization
Reservoir characterization also benefits from simulation technologies. It aids in understanding the structural and geological features of the reservoir, allowing for improved control of drilling operations and reservoir performance.
Conclusion
Vertical drilling is still an important and commonly utilized technology in the oil and gas industry, providing a direct route to the Earth’s massive energy reserves. The benefits of simulation in vertical drilling are likely to expand as technology advances, making drilling operations more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible, ensuring that this critical technique will continue to play a central role in meeting the world’s energy needs for years to come.
