Understanding Plug and Abandonment in the Oil and Gas Industry: Safeguarding Environment and Public Health
Plug and abandonment plays a vital role in the lifecycle of oil and gas wells, marking the end of their operational phase. As the industry adapts to evolving environmental standards and operational challenges, understanding the intricacies of plug and abandonment (P&A) becomes ever more essential.
What is Plug and Abandonment

At its core, plug and abandonment refers to the process of permanently sealing an oil or gas well that is no longer productive or economically viable. This process is essential for mitigating environmental risks, ensuring safety, and complying with regulatory requirements. Properly executed plug and abandonment procedures are paramount to prevent potential hazards such as groundwater contamination, methane leakage, and surface hazards.
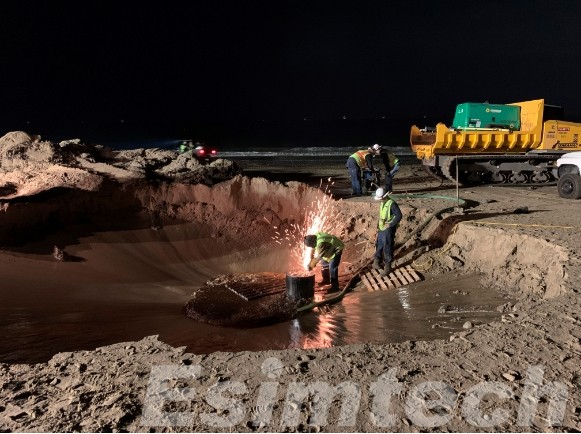

The Importance of Plug and Abandonment
The importance of plug and abandonment cannot be overstated. With thousands of wells worldwide reaching the end of their productive lives each year, safe and effective abandonment practices are critical for environmental protection and public safety. Abandoned wells, if not properly sealed, can become conduits for environmental contamination and methane emissions, contributing to climate change and posing risks to surrounding communities and ecosystems.

The Process of Plug and Abandonment
1. Well Evaluation
Before embarking on plug and abandonment, a comprehensive evaluation of the well is conducted. This involves assessing the structural integrity of the wellbore, evaluating the condition of casing and cement, and analyzing geological data to determine the appropriate abandonment strategy. Well logs, pressure tests, and site inspections are among the tools utilized during this phase.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the regulatory landscape is a crucial aspect of plug and abandonment. Operators must adhere to local, state, and federal regulations governing well closure, including environmental protection standards and safety protocols. Obtaining the necessary permits and approvals is essential before commencing abandonment activities.
3. Plugging
The plugging phase involves the installation of mechanical barriers, or plugs, at strategic intervals within the wellbore to prevent fluid migration. These plugs, typically made of cement or specialized materials, are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures. The placement of plugs is guided by well geometry, formation characteristics, and regulatory requirements.
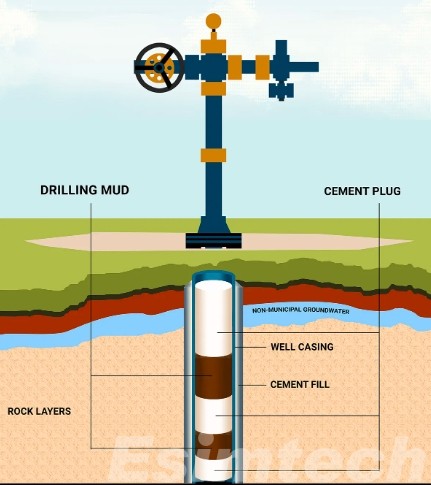
4. Cementing
Cementing is a critical step in the plug and abandonment process, ensuring the integrity of the plugs and providing additional sealing along the wellbore. Cement slurry is pumped into the annular space between the casing and the formation, filling voids and creating a secure barrier. Proper cement placement and bonding are essential to prevent fluid migration and maintain well integrity.
5. Verification and Testing
Following cementing, verification tests are conducted to confirm the effectiveness of the plugging and sealing barriers. Pressure tests, temperature measurements, and acoustic logging may be performed to assess the integrity of the cement sheath and detect any potential leaks or weaknesses. These tests help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and provide assurance of long-term well integrity.
6. Surface Restoration
Once the wellbore is securely plugged and verified, surface equipment and infrastructure are removed or decommissioned in accordance with regulatory guidelines. This may include dismantling production facilities, removing wellhead equipment, and restoring the site to its natural state or alternative land use. Surface restoration efforts aim to minimize the visual impact and environmental footprint of the abandoned well site.
7. Monitoring and Compliance
Even after plug and abandonment activities are completed, ongoing monitoring and compliance are necessary to verify the effectiveness of the closure and detect any potential issues. Regulatory agencies may require periodic inspections, environmental monitoring, and reporting to ensure continued compliance with closure standards and regulations.
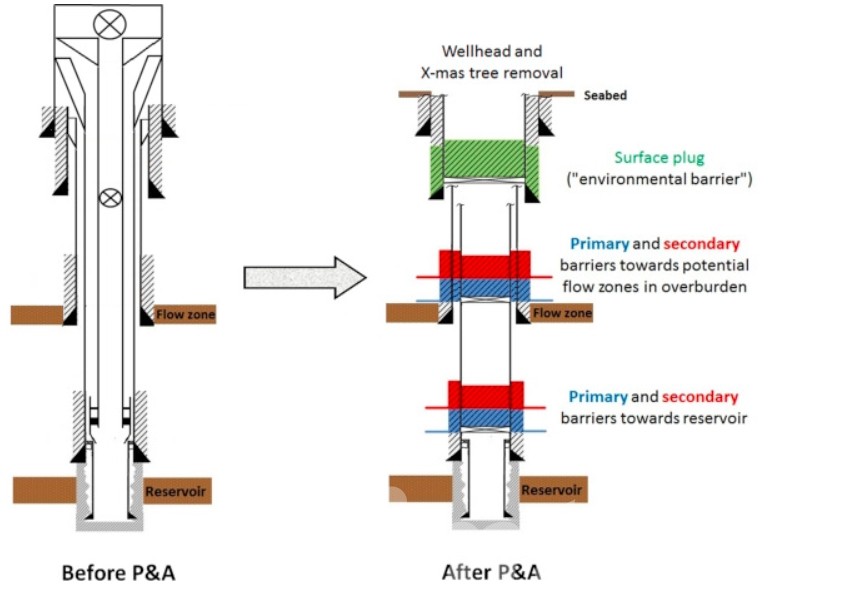
Challenges and Innovative Solutions in Plug and Abandonment
Executing P&A activities comes with its own set of challenges, ranging from technical complexities to environmental concerns. To address these challenges, the industry is continuously exploring innovative solutions that enhance safety, efficiency, and environmental stewardship throughout the plug and abandonment process.
Challenges
1. Well Integrity
Ensuring the integrity of wellbore barriers during plug and abandonment is crucial to prevent fluid migration and environmental contamination. However, aging infrastructure, corrosion, and wellbore integrity issues pose significant challenges to effective well closure.
2. Cost Constraints
P&A operations can be costly, especially for wells located in remote or challenging environments. Operators must navigate budget constraints while adhering to regulatory requirements and industry best practices for safe well closure.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Meeting stringent regulatory requirements for plug and abandonment is a complex undertaking, involving permits, reporting, and compliance with environmental and safety standards. Regulatory uncertainty and evolving regulations add further challenges to the process.
4. Environmental Risks
Improperly abandoned wells can pose environmental risks, including groundwater contamination and methane emissions. Achieving effective zonal isolation and mitigating these risks requires careful planning and execution of P&A activities.
Innovative Solutions
1. Advanced Materials and Technologies
Innovations in materials, such as engineered cements and polymer-based sealants, offer improved zonal isolation and long-term integrity for wellbore barriers. Advanced downhole tools and technologies, including casing milling systems and robotic platforms, enable precise placement of plugs and barriers in challenging wellbore conditions.
2. Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling allows operators to assess well integrity, identify potential risks, and optimize P&A strategies. Real-time monitoring systems, including fiber-optic sensing and distributed temperature sensing, provide continuous feedback on well conditions, enabling proactive intervention and maintenance.
3. Collaborative Partnerships
Collaborative partnerships between industry stakeholders, regulatory agencies, and research institutions facilitate knowledge-sharing and innovation in P&A practices. Joint research projects, technology consortia, and industry forums promote the development of standardized protocols and best practices for safe and efficient well closure.
4. Remediation and Site Rehabilitation
Innovations in remediation technologies, such as in-situ chemical oxidation and microbial treatments, offer environmentally sustainable solutions for addressing contamination at abandoned well sites. Additionally, advanced land reclamation techniques, including revegetation and soil stabilization, restore abandoned well sites to their natural or alternative land uses.
5. Regulatory Reform and Standards Development
Engaging with regulatory authorities to streamline permitting processes and develop risk-based regulations for P&A activities enhances regulatory certainty and promotes consistency in closure practices. Clearer guidelines and standards facilitate compliance and encourage innovation in well closure technologies and practices.
Key Ways in Which Simulation Technology is Used in Plug and Abandonment
Simulation technology is increasingly being utilized in plug and abandonment (P&A) operations within the oil and gas industry to enhance safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This technology allows operators to digitally model and simulate various aspects of the P&A process, from wellbore conditions to cementing procedures, enabling better decision-making and optimization of resources.

1. Wellbore Integrity Assessment
Simulation software enables operators to assess the structural integrity of wellbores before and during plug and abandonment operations. By modeling wellbore conditions, including casing corrosion, cement degradation, and formation characteristics, operators can identify potential integrity issues and plan remediation strategies accordingly. This proactive approach helps prevent unplanned events during P&A activities.
2. Cementing Design and Optimization
Simulation tools allow operators to design and optimize cementing jobs for P&A operations. By modeling cement slurry properties, fluid rheology, and downhole conditions, operators can determine the most effective cementing recipes and placement strategies to achieve zonal isolation and wellbore integrity. Simulation also helps predict cement placement effectiveness, reducing the risk of cement channeling or inadequate coverage.
3. Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Simulation technology enables operators to conduct comprehensive risk assessments for plug and abandonment operations. By simulating various scenarios, including wellbore failures, pressure anomalies, and environmental risks, operators can identify potential hazards and develop mitigation strategies to minimize risks to personnel, equipment, and the environment. This proactive risk management approach enhances safety and regulatory compliance.
4. Equipment Performance and Reliability
Simulation software allows operators to simulate the performance and reliability of equipment used in P&A operations, such as downhole tools, cementing units, and well control systems. By modeling equipment behavior under different operating conditions and failure scenarios, operators can assess performance limitations, optimize equipment selection, and plan contingency measures to ensure smooth and efficient operations.
5. Training and Skills Development
Simulation technology provides a valuable training and skills development tool for personnel involved in plug and abandonment operations. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) simulations allow operators to simulate realistic P&A scenarios in a safe and controlled environment, providing hands-on training for wellsite personnel, engineers, and supervisors. This immersive training experience enhances competency, improves decision-making skills, and fosters collaboration among team members.
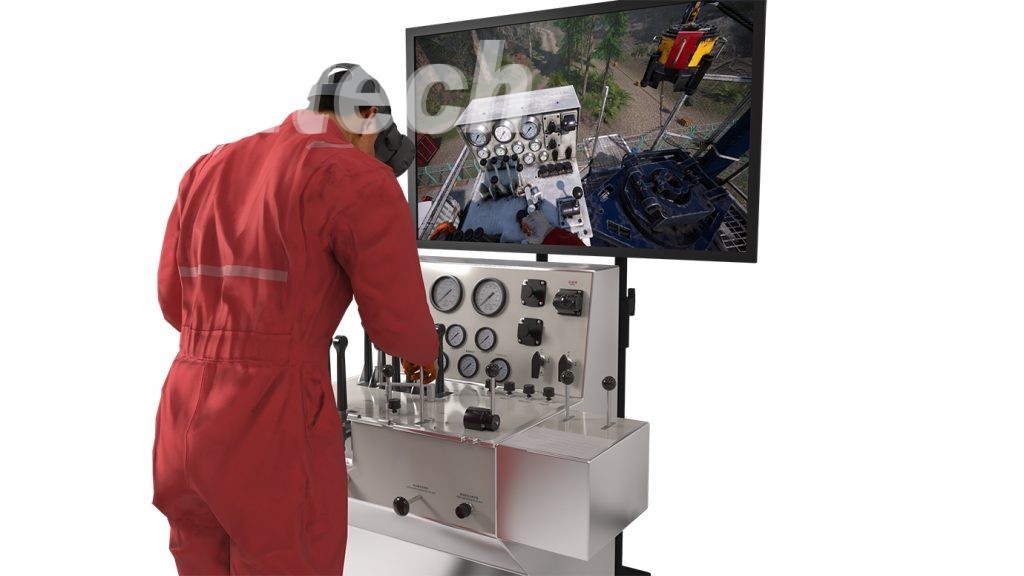

6. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Simulation software enables real-time monitoring and optimization of plug and abandonment. By integrating data from downhole sensors, surface equipment, and simulation models, operators can track operational parameters, detect deviations from planned procedures, and make timely adjustments to optimize performance and efficiency. This data-driven approach improves operational decision-making and reduces downtime and costs associated with P&A activities.
Conclusion
Proper abandonment of oil wells is essential to safeguarding both the environment and public health. By prioritizing responsible plug and abandonment practices and embracing technological innovation, the industry can ensure a sustainable future while upholding its commitment to safety and environmental protection.
Simulation technology is a valuable tool in plug and abandonment operations within the oil and gas industry, through which, Operators can enhance safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness throughout the P&A process, ultimately ensuring the safe and environmentally responsible closure of oil and gas wells.

