Understanding Conventional Rotary Drilling: Pros,Cons and What are Its Alternatives
Conventional rotary drilling is the most common type of drilling used in the oil and gas industry. It involves rotating a drill bit at the end of a drill string to penetrate the earth. The drill string is made up of a series of hollow pipes that are connected together. Drilling fluid is pumped down the drill string and out of the drill bit to cool and lubricate the bit, remove cuttings, and maintain hydrostatic pressure.
The drill bit is rotated by a top drive, which is a powerful electric motor that is mounted at the top of the drill rig. The top drive transmits torque through the drill string to the drill bit. As the drill bit rotates, it cuts into the earth, creating a wellbore.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Rotary Drilling
Advantages of Conventional Rotary Drilling
Versatile and reliable: Conventional rotary drilling can be used to drill a wide variety of wells, including oil and gas wells, water wells, geothermal wells, environmental wells, and construction wells. It is also well-suited for drilling in a variety of formations, from soft to hard.
Relatively simple and inexpensive: Conventional rotary drilling is a relatively simple and inexpensive drilling method. The equipment and expertise required are widely available, and the drilling process is well-understood.
Disadvantages of Conventional Rotary Drilling
Can be slow and expensive, especially when drilling deep wells: Conventional rotary drilling can be a slow and expensive process, especially when drilling deep wells. The drill bit must be rotated continuously, and a large amount of drilling fluid must be pumped down the wellbore.
Not well-suited for drilling in complex or challenging formations: Conventional rotary drilling is not well-suited for drilling in complex or challenging formations, such as formations with high levels of H2S or formations with narrow pressure margins. In these cases, more specialized drilling methods are required.
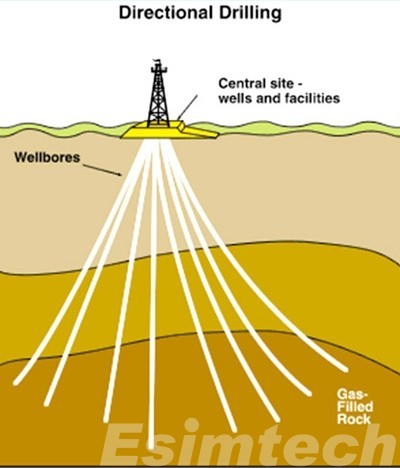
Alternatives to Conventional Rotary Drilling
In recent years, a number of alternatives to conventional rotary drilling have been developed. These alternatives are designed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of drilling, particularly in complex or challenging formations.
Some of the most common alternatives to conventional rotary drilling include:
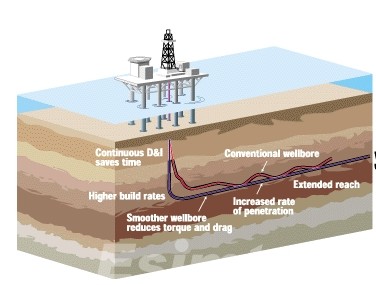
- Directional drilling: Directional drilling allows operators to drill wells that deviate from the vertical plane. This is useful for drilling wells that target reservoirs that are located at an angle or that are buried deep below the surface. Directional drilling can also be used to drill multiple wells from a single drilling pad.
- Horizontal drilling: Horizontal drilling is a type of directional drilling that is used to drill wells that are parallel to the surface. This is useful for drilling wells in unconventional reservoirs, such as shale and tight oil formations.
- MPD (Managed Pressure Drilling): MPD is a technique that allows operators to precisely control the pressure in the wellbore. This is useful for drilling in wells with narrow pressure margins or in wells with high levels of H2S (hydrogen sulfide).
- UFD (Underbalanced Drilling): UFD is a technique that involves drilling a well with a lower pressure in the wellbore than the pressure in the surrounding formation. This is useful for drilling in wells with high reservoir pressure or in wells with low permeability.
- Coiled tubing drilling (CTD): CTD is a method of drilling that uses coiled tubing instead of drill pipe. This is useful for drilling in shallow wells or in wells with complex trajectories.
- Percussion drilling: Percussion drilling is a method of drilling that uses a hammer to drive a drill bit into the ground. This is useful for drilling in hard formations or in formations with a lot of debris.
- Laser drilling: Laser drilling is a method of drilling that uses a laser to cut through the formation. This is useful for drilling in very hard formations or in formations that are sensitive to heat.
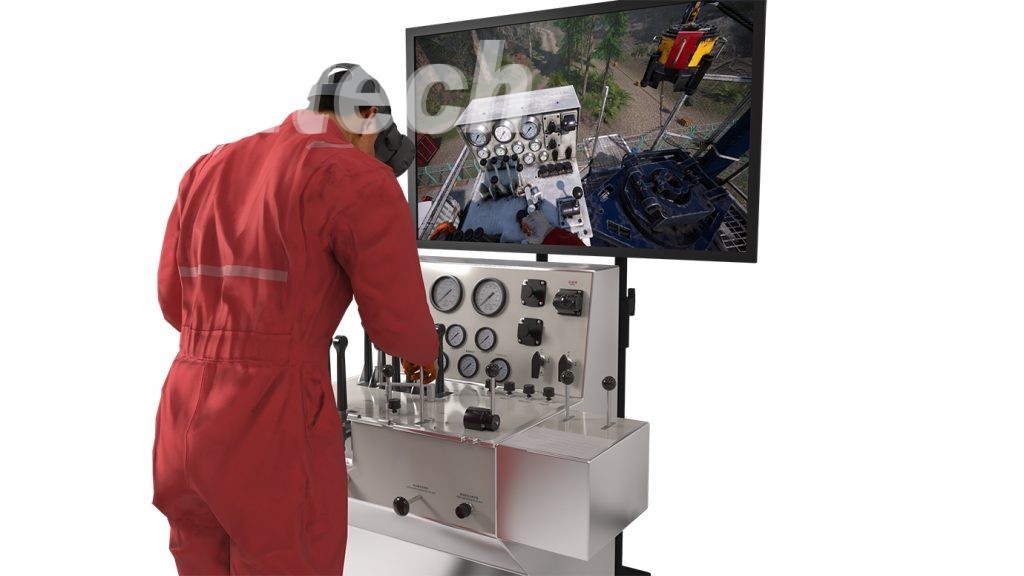
Application of Oil and Gas Drilling Simulation
Oil and gas drilling simulation is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of drilling operations. It can be used to:
- Plan and design wells: Drilling simulation can be used to model the drilling process and predict the performance of different drilling methods and equipment. This information can be used to design wells that are optimized for safety, efficiency, and cost.
- Train drill crews: Drilling simulation can be used to train drill crews on how to operate different drilling equipment and respond to different drilling scenarios. This can help to improve safety and efficiency on the drilling rig.
- Monitor and troubleshoot drilling operations: Drilling simulation can be used to monitor drilling operations in real time and identify potential problems before they occur. This can help to prevent drilling accidents and reduce costs.
- Optimize drilling parameters: Drilling simulation can be used to optimize drilling parameters, such as weight on bit, rotary speed, and mud flow rate. This can help to improve drilling performance and reduce costs.

Conclusion
Conventional rotary drilling is the most common type of drilling in the oil and gas industry, but it has limitations. Alternatives, such as directional drilling, horizontal drilling, managed pressure drilling, and underbalanced drilling, offer advantages such as improved efficiency, increased production rates, and reduced risk.
Oil and gas drilling simulation is a powerful tool that can improve the safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of drilling operations by planning and designing wells, training drill crews, monitoring and troubleshooting drilling operations, and optimizing drilling parameters.
The future of oil and gas drilling is likely to be characterized by a continued shift towards more advanced and efficient drilling methods, with alternatives to conventional rotary drilling and oil and gas drilling simulation playing a major role.

