The Essential Role of the Drilling Mud System in Modern Drilling Operations
The drilling mud system, often likened to the circulatory system of a drilling operation, is an essential component that ensures the efficiency, safety, and success of drilling projects, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining wellbore stability, transporting drill cuttings, and managing pressure. This article delves into the components, functions, and significance of the drilling mud system in contemporary drilling practices.
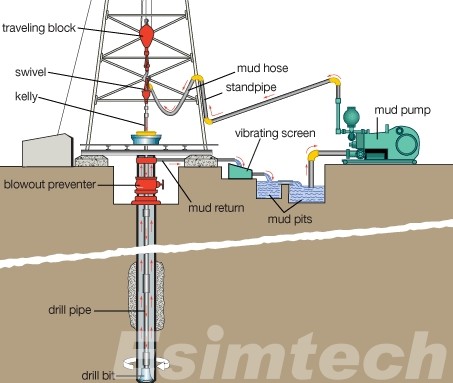
Components of the Drilling Mud System
1. Mud Tanks
Function: Storage and Mixing
- Description: Mud tanks are large containers used to store and mix the drilling mud. They are the initial point where the drilling fluids are prepared and maintained.
- Importance: Proper mixing and storage in mud tanks ensure that the drilling fluid has the correct properties before it is pumped down the wellbore.
2. Shale Shakers
Function: Primary Solids Control
- Description: Shale shakers are vibrating screens that remove large drill cuttings from the circulating drilling mud.
- Importance: By separating solids from the fluid, shale shakers prevent the accumulation of drill cuttings in the mud, ensuring efficient drilling and preventing blockages.
3. Degassers
Function: Gas Removal
- Description: Degassers are devices that remove gas entrained in the drilling mud, such as methane or hydrogen sulfide.
- Importance: Removing gas from the mud is crucial for maintaining its density and stability, which is essential for pressure control and safe drilling operations.
4. Desanders and Desilters
Function: Secondary Solids Control
- Description: Desanders and desilters are used to remove finer particles from the drilling mud. Desanders typically remove particles larger than 50 microns, while desilters handle particles down to 20 microns.
- Importance: These units help ensure that the drilling mud remains clean and free of fine solids, which can affect its performance and the efficiency of the drilling process.
5. Mud Pumps
Function: Circulation
- Description: Mud pumps are heavy-duty pumps that circulate the drilling mud from the mud tanks through the drill string and back to the surface.
- Importance: These pumps must handle high pressures and flow rates to ensure that the mud is continuously circulated, cooling the drill bit, and transporting cuttings to the surface.
6. Mixing Hoppers
Function: Additive Mixing
- Description: Mixing hoppers are used to add chemicals and other additives to the drilling mud to adjust its properties, such as viscosity, density, and pH.
- Importance: Proper mixing of additives ensures that the drilling mud has the desired characteristics to support drilling operations and manage wellbore conditions.

7. Centrifuges
Function: Fine Solids Removal
- Description: Centrifuges spin the drilling fluid to separate out the finest particles and reclaim barite, a weighting agent used in the mud.
- Importance: By removing fine solids, centrifuges help maintain the desired mud properties and reduce waste, enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the drilling process.
8. Mud Cleaners
Function: Combined Solids Control
- Description: Mud cleaners combine the functions of shale shakers, desanders, and desilters. They use a combination of hydrocyclones and vibrating screens.
- Importance: They provide a comprehensive solution for removing both large and fine solids, improving the quality and performance of the drilling mud.
9. Mud Agitators
Function: Mixing and Suspension
- Description: Mud agitators are mechanical devices used to keep the drilling mud and its additives properly mixed in the mud tanks.
- Importance: Ensuring homogeneity of the drilling mud is critical for consistent performance and preventing the settling of solids.
10. Mud Gas Separators
Function: Large Gas Bubble Removal
- Description: Mud gas separators remove large gas bubbles from the drilling mud before it reaches the shale shakers.
- Importance: This helps to control wellbore pressure and prevent dangerous situations such as well blowouts.
11. Flow Meters and Sensors
Function: Monitoring and Control
- Description: These devices measure the flow rate, density, and other properties of the drilling mud in real-time.
- Importance: Real-time monitoring allows for immediate adjustments to maintain optimal drilling conditions and prevent problems.
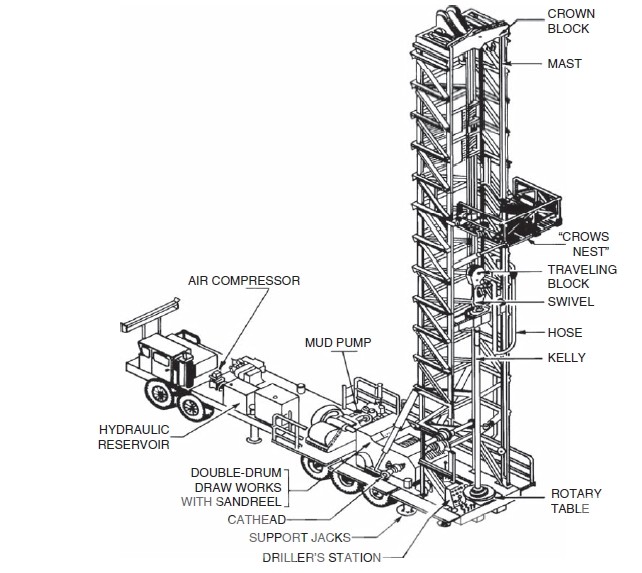
Importance of the Drilling Mud System
1. Operational Efficiency
- Continuous Drilling: The drilling mud system ensures the continuous removal of drill cuttings from the wellbore, preventing blockages and allowing uninterrupted drilling.
- Enhanced Drilling Performance: By cooling and lubricating the drill bit, the system reduces wear and tear on equipment, leading to longer bit life and fewer interruptions.
- Optimized Mud Properties: The ability to adjust the properties of the drilling mud, such as viscosity and density, ensures that the mud meets the specific requirements of the drilling operation, enhancing overall performance.
2. Safety
- Pressure Control: Properly managed drilling mud balances the pressure within the wellbore, preventing blowouts and uncontrolled fluid flows that could pose serious safety hazards.
- Wellbore Stability: The drilling mud stabilizes the wellbore walls, preventing collapse and ensuring the structural integrity of the well, which is crucial for the safety of the operation.
- Gas Management: Degassers and mud gas separators remove hazardous gases from the drilling mud, reducing the risk of dangerous gas build-ups and explosions.
3. Environmental Protection
- Minimized Environmental Impact: Effective management of drilling fluids and cuttings reduces the environmental footprint of drilling operations. Proper disposal and recycling practices are integral to minimizing pollution.
- Reduced Fluid Loss: The formation of a filter cake on the wellbore walls by the drilling mud helps control fluid loss into the formation, protecting subsurface environments from contamination.
- Recycling and Reclamation: Reclaiming and reusing drilling mud components, such as barite, not only reduces costs but also minimizes waste generation, contributing to more sustainable drilling practices.
4. Economic Efficiency
- Cost Savings: Efficient solids control and fluid management reduce the costs associated with drilling fluid consumption and waste disposal.
- Reduced Downtime: By preventing issues such as wellbore collapse and equipment wear, the drilling mud system minimizes downtime, leading to significant cost savings over the course of a drilling project.
- Optimized Resource Use: Effective mud systems optimize the use of additives and weighting agents, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and economically.
5. Data and Decision-Making Support
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced sensors and data analytics integrated into the drilling mud system provide real-time data on mud properties and wellbore conditions, enabling informed decision-making and immediate adjustments.
- Enhanced Control: The ability to monitor and control mud properties in real-time allows for precise management of drilling operations, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
Key Technological Advancements in Drilling Mud Systems
The drilling mud system has seen significant technological advancements in recent years, enhancing its efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. These innovations are transforming how drilling operations are conducted, making them more effective and environmentally friendly.
1. Synthetic-Based Muds (SBMs)
- Description: Synthetic-based muds are engineered fluids that serve as an alternative to traditional oil-based muds.
- Advantages: SBMs offer similar performance characteristics to oil-based muds but with lower environmental risks. They are less toxic, biodegradable, and reduce the impact on marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
2. Nanotechnology
- Description: Incorporation of nanoparticles into drilling fluids to enhance their properties.
- Advantages: Nanoparticles improve the drilling mud’s ability to stabilize the wellbore, carry cuttings, and manage fluid loss. They also enhance thermal stability and rheological properties, leading to more efficient drilling operations.
3. Real-Time Monitoring Systems
- Description: Advanced sensors and data analytics tools that provide real-time monitoring of drilling mud properties and wellbore conditions.
- Advantages: These systems enable immediate adjustments to mud properties, optimizing drilling performance and safety. Real-time data allows for precise control over the drilling process, reducing the risk of blowouts and other hazardous events.
4. Automated Mud Mixing Systems
- Description: Computer-controlled systems that automate the mixing of drilling fluids and additives.
- Advantages: Automation ensures consistent mud properties and reduces human error. These systems can quickly adjust the composition of drilling fluids in response to changing well conditions, improving operational efficiency.
5. Advanced Solids Control Equipment
- Description: Enhanced shale shakers, centrifuges, and other solids control devices designed to more effectively separate drill cuttings from drilling mud.
- Advantages: Improved solids control increases the lifespan of drilling fluids and reduces waste. This leads to cost savings and minimizes the environmental impact of drilling operations.

6. Eco-Friendly Additives
- Description: Development of environmentally friendly additives for drilling muds.
- Advantages: These additives reduce the ecological footprint of drilling operations. They are often biodegradable and non-toxic, making the disposal of used drilling fluids safer for the environment.
7. Enhanced Filtration Systems
- Description: Advanced filtration technologies that improve the removal of fine particles from drilling mud.
- Advantages: Better filtration systems maintain the quality of the drilling mud, enhancing its performance and reducing the risk of formation damage. They also help in reclaiming valuable components like barite.
8. Intelligent Mud Pumps
- Description: Smart pumps equipped with sensors and control systems that adjust their operation based on real-time data.
- Advantages: Intelligent mud pumps optimize the circulation of drilling fluids, reducing energy consumption and improving the efficiency of the drilling process. They can automatically adapt to changes in well conditions, ensuring consistent performance.
9. High-Performance Mud Motors
- Description: Mud motors designed to operate effectively with modern drilling fluids.
- Advantages: These motors improve the efficiency of directional drilling operations, enhancing the ability to reach complex targets. They are designed to work with a variety of drilling muds, including high-density and high-viscosity fluids.
10. Digital Twins
- Description: Virtual drilling simulators can simulate the performance of the drilling mud system under various conditions.
- Advantages: Digital twins allow for the testing and optimization of mud systems in a virtual environment before implementation in the field. This leads to better design and operation strategies, reducing risks and improving overall efficiency.

Conclusion
The drilling mud system is the lifeblood of modern drilling operations, performing multiple critical functions that ensure efficiency, safety, and environmental protection. As technology advances, the system continues to evolve, offering improved performance and sustainability in the demanding environment of drilling. Understanding and optimizing the components and functions of the drilling mud system is essential for the success of any drilling project.
