Oil and Gas Simulation: Operations Process
The oil and gas industry is a complex and highly dynamic field, requiring careful planning, precise execution, and constant adaptation to changing conditions. To navigate these challenges, companies have increasingly turned to oil and gas simulation technologies, which play a critical role in optimizing operations, reducing risks, and improving decision-making. This article explores how simulation is utilized in the oil and gas industry, focusing on its impact on the operations process.
Exploration Stage Simulation
The exploration stage is the first and one of the most critical phases in the oil and gas value chain. This stage involves identifying potential sites where oil and gas reserves might be located. The process typically includes geological surveys, seismic data collection, and interpretation.
Simulations in this stage:
- Exploration simulations help geologists and geophysicists model subsurface structures based on seismic data, well logs, and other geological information. These simulations can predict the likelihood of finding hydrocarbons, estimate reserve sizes, and assess the potential productivity of a site. By simulating different scenarios, exploration teams can optimize the placement of wells, minimize dry wells, and make informed decisions about where to allocate resources for further exploration.
- Advanced 3D and 4D seismic simulations, for instance, allow operators to visualize the subsurface in three dimensions and monitor changes over time (4D). This helps in identifying the most promising drilling targets and reduces the risks associated with exploration activities.
Drilling Stage Simulation
Once a potential site has been identified, the drilling stage begins. This phase involves creating a borehole to access the oil and gas reserves beneath the earth’s surface. Drilling operations are complex, requiring careful planning and precise execution to avoid costly mistakes and ensure safety.
Simulations in this stage:
- Drilling simulations play a critical role in training drillers and engineers, allowing them to practice and refine drilling techniques in a virtual environment before executing them in the field. These simulations can replicate a wide range of drilling conditions, including different types of rock formations, pressure scenarios, and equipment configurations.
- For instance, drillers can use simulations to test different drilling mud compositions, optimize drilling speed, and evaluate the impact of various drilling parameters on well stability. By simulating potential problems such as blowouts, stuck pipe, or lost circulation, teams can develop strategies to mitigate these risks in real-world operations.
- In addition to training, drilling simulations are used in real-time operations to monitor and adjust drilling parameters, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing non-productive time.

Mining and Production Stage Simulation
After drilling is completed, the focus shifts to extracting hydrocarbons from the reservoir. This stage, known as mining and production, involves completing wells, installing production equipment, and managing the reservoir to ensure steady output.
Simulations in this stage:
- Production simulations are vital for optimizing reservoir behavior over time. Engineers use these tools to model the flow of oil and gas, predict production rates, and choose the best extraction methods. By simulating scenarios like water flooding or gas injection, operators can identify the most effective techniques to maximize recovery.

- Reservoir simulations also help manage pressure and flow, ensuring efficient production. Engineers can test different production rates and recovery methods to extend the reservoir’s life and optimize output.
- These simulations are also used to design and refine surface facilities like separators and storage units. By testing processes virtually, operators can avoid costly mistakes and downtime.
In summary, mining and production simulations are essential for maximizing recovery, optimizing production, and ensuring efficient, long-term operations.
Processing and Transportation Stage Simulation
After hydrocarbons are extracted, they must be efficiently processed and transported. The use of simulations in this stage focuses on optimizing these complex operations.
- Process Optimization:
- Simulations help design and fine-tune processing facilities such as separators, distillation columns, and refining units.
- They allow engineers to model fluid dynamics, chemical reactions, and heat transfer processes.
- By testing different conditions, operators can maximize efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and lower emissions.
- Pipeline and Transportation Modeling:
- Simulations predict the behavior of hydrocarbons in pipelines, considering factors like pressure, temperature, and flow conditions.
- This helps in designing pipelines that minimize blockages and optimize energy use.
- Transportation logistics can also be simulated, factoring in route optimization, weather, and geopolitical risks.

- Environmental Management:
- Simulations assess the environmental impact of processing and transportation activities.
- They help operators plan for minimizing emissions, spill risks, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Cost and Safety Enhancements:
By simulating various scenarios, companies can reduce costs by improving operational efficiency.
Safety is enhanced by identifying and mitigating risks in both processing and transportation stages.
Safety and Compliance Training
Safety and compliance are paramount in the oil and gas industry due to the inherent risks involved in handling hydrocarbons. Simulations play a crucial role in preparing personnel and ensuring adherence to industry regulations.
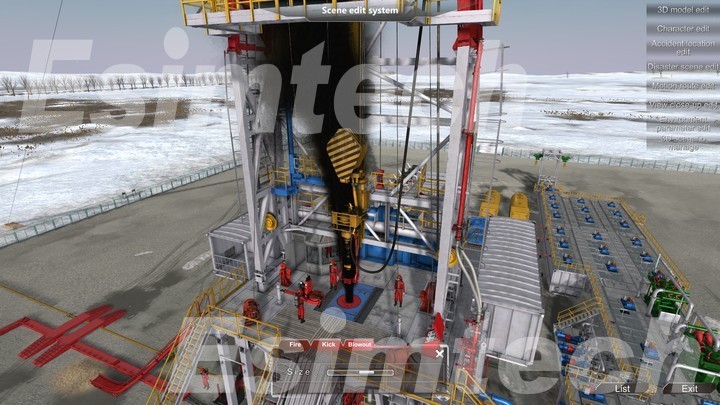
- Emergency Response Training:
- Simulations provide realistic scenarios for emergency situations such as blowouts, fires, chemical spills, and evacuations.
- Workers can practice responding to these emergencies in a controlled, virtual environment, which helps them develop quick, effective responses in real-life situations.
- Offshore platform workers, for example, can rehearse evacuation drills that simulate challenging conditions like limited visibility and rough seas.

- Safe Work Practices:
- Simulations train employees on proper handling of hazardous materials, correct lifting techniques, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- These simulations ensure that workers are familiar with safe work practices and can perform their duties without compromising safety.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Compliance simulations educate workers on industry regulations, environmental standards, and safety protocols.
- They help ensure that all personnel understand and adhere to legal requirements, reducing the risk of violations and associated penalties.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Simulations allow for ongoing training and refresher courses, helping workers stay updated on best practices and new regulations.
- This continuous learning approach ensures that safety and compliance are maintained at the highest levels throughout all operations.
- Risk Mitigation:
- By simulating potential hazards and compliance scenarios, companies can identify and address risks proactively, reducing the likelihood of accidents and ensuring a safer work environment.
Conclusion
Simulation technologies are crucial in the oil and gas industry, enhancing efficiency, safety, and decision-making across all stages—from exploration to transportation. These tools optimize operations, reduce risks, and ensure compliance with industry standards. As the industry evolves, the importance of simulations in driving innovation and maintaining operational excellence will continue to grow.
