How to Ensure Effective Well Abandonment
Well abandonment is a critical process in the lifecycle of oil and gas wells, marking the final stage when a well is permanently taken out of service. As the global energy industry evolves and older wells reach the end of their productive lives, proper well abandonment has become increasingly important to ensure environmental safety, protect public health, and mitigate long-term risks. This article explores the process of well abandonment, its significance, challenges, and the measures needed to ensure it is carried out effectively.

What is Well Abandonment
Well abandonment refers to the process of permanently sealing a well that is no longer in use or economically viable. This process is designed to prevent the leakage of oil, gas, or other fluids into the environment, ensuring that the well does not pose a threat to groundwater, surface ecosystems, or the atmosphere. Proper abandonment involves a series of technical steps, including the removal of equipment, cleaning the wellbore, and sealing it with materials such as cement to isolate underground formations.

Types of Well Abandonment
1. Temporary Abandonment
Temporary abandonment occurs when a well is shut down for a limited time but may be reactivated in the future. This type of abandonment involves securing the well with mechanical barriers and cement plugs while maintaining the infrastructure intact for potential future use. It is commonly used when market conditions change or when further exploration is planned.
2. Suspended Abandonment
Suspended abandonment refers to wells that are inactive for an extended period but still under monitoring. While similar to temporary abandonment, it involves more robust sealing methods to ensure long-term well integrity. Operators choose suspended abandonment when the well still holds potential resources but is not currently economically viable to operate.
3. Permanent Abandonment
Permanent abandonment, on the other hand, signifies the complete and irreversible closure of a well. This process involves placing multiple layers of cement plugs to isolate different geological formations, removing surface infrastructure, and restoring the site. Permanent abandonment is carried out when a well is no longer productive or poses environmental risks if left open.
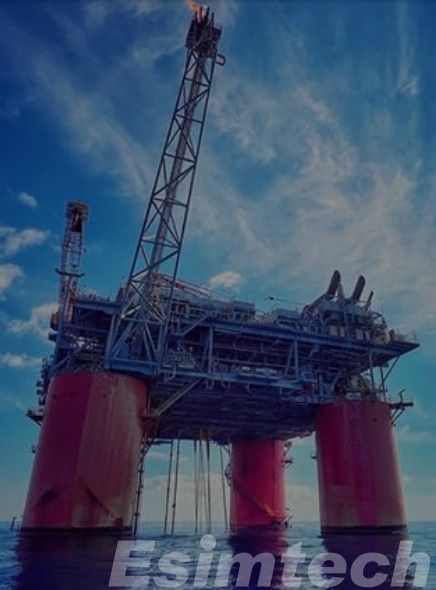

Why Well Abandonment is Important in the Oil and Gas Industry
- Environmental Protection
One of the most critical reasons for proper well abandonment is to prevent environmental contamination. An improperly abandoned well can leak hydrocarbons, gas, or other toxic substances into the surrounding environment, leading to groundwater contamination, soil pollution, or surface spills. Proper abandonment ensures that no fluids or gases escape from the well, which helps protect ecosystems and surrounding communities.
- Public Health and Safety
Abandoned wells that are not properly sealed can become a safety hazard. They may present risks such as uncontrolled gas leaks, well blowouts, or even fires and explosions if not closed safely. By following proper abandonment procedures, these risks are minimized, ensuring the safety of personnel and local communities near the well site.
- Regulatory Compliance
Oil and gas operators are required by law to properly abandon wells to comply with local, state, and federal regulations. These regulations are put in place to protect public health, the environment, and the broader industry. Failing to properly abandon a well can lead to substantial fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage for operators.
- Preventing Long-Term Liability
If a well is not abandoned correctly, the operator could remain liable for any environmental damage or accidents that occur in the future. Improper abandonment can result in costly remediation work, legal proceedings, and damage to the operator’s reputation. By properly abandoning the well, operators can close the well safely and limit long-term liabilities.
- Protecting Natural Resources
When a well is abandoned, the surrounding groundwater and land resources must be protected. Improper abandonment can cause contamination of drinking water sources or damage to agricultural land. By following industry standards for abandonment, operators help safeguard these critical natural resources for the future.
- Maintaining Industry Integrity
Proper well abandonment contributes to the overall integrity and sustainability of the oil and gas industry. It demonstrates the industry’s commitment to environmental stewardship, safety, and regulatory compliance, which helps maintain public trust and supports the continued operation of oil and gas activities.

Key Steps in the Well Abandonment Process
The process of well abandonment is complex and involves multiple steps that are carefully planned and executed.
Step 1: Planning and Assessment
Before any physical work can begin, a thorough evaluation of the well’s current state must take place. This assessment includes reviewing the well’s history, checking for any signs of structural damage, and performing integrity tests to confirm that the well can be safely sealed. An environmental impact assessment (EIA) may also be conducted to identify any potential risks or environmental concerns that need to be addressed during the abandonment process.
Step 2: Plugging the Well
This step is critical to ensuring that hydrocarbons, water, or gas do not flow from the well after abandonment. Typically, a series of cement plugs are set at specific intervals within the well to seal off the flow of fluids. These plugs are designed to isolate the different pressure zones within the wellbore and prevent any escape of substances. After the plugs are placed, pressure testing is performed to verify that the plugs are properly sealed and stable.
After sealing the well, the wellhead equipment, such as valves and Christmas trees, is removed. This ensures that no equipment remains to obstruct the sealing process. At this point, the well is permanently shut off, and any potential routes for future fluid migration are blocked.
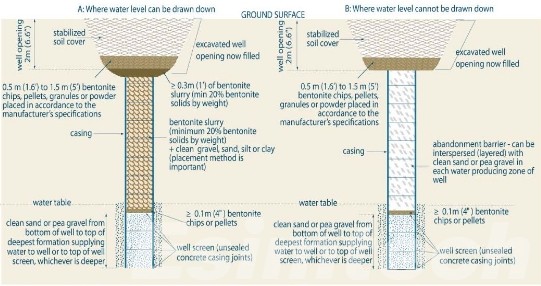
Step 3: Surface Restoration
Once the well itself has been sealed, attention turns to the surface restoration phase. This step is essential to mitigate any environmental damage caused by the drilling and production activities. The well site is cleared of any infrastructure, equipment, and waste materials. The area is then restored, often involving reseeding the land with native vegetation or performing other remediation techniques to return the land to its natural state. In some cases, particularly in offshore locations, more complex environmental monitoring may be required to ensure that there are no lasting impacts.
Regulations and Standards in Well Abandonment
Well abandonment is governed by strict industry regulations, which vary by region. These regulations are enforced by government agencies and regulatory bodies to ensure that proper procedures are followed. Some key regulations include:
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides guidelines for the proper abandonment of oil and gas wells, including API RP 65 for wellbore construction and abandonment.
- Local Regulations: Different countries and states have their own laws, which may include specific requirements for the depth of the plugs, type of materials used, and environmental monitoring post-abandonment.
- Environmental Protection Laws: Regulations like the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) in the U.S. ensure that environmental impact assessments are carried out and that operators follow specific steps for land restoration.

Challenges and Best Practices in Well Abandonment
| Challenge | Description | Best Practice |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensuring all local and international regulations and standards are met. | Stay updated on regulations; collaborate with regulatory bodies for compliance. |
| Wellbore Integrity | Managing the risk of leakage, particularly in aging or poorly maintained wells. | Conduct thorough well inspections and apply advanced well integrity tools. |
| Sealing and Plugging | Properly sealing the well to prevent contamination or leakage of fluids. | Use multiple barriers; ensure correct materials and techniques for plugging. |
| Equipment Wear and Tear | Managing the degradation of tools and equipment used in the abandonment process. | Regularly inspect and replace equipment to minimize downtime and failure. |
| Environmental Impact | Mitigating risks of environmental contamination from residual hydrocarbons. | Adopt environmentally friendly techniques; perform comprehensive spill response plans. |
| Cost Management | Keeping abandonment costs within budget, especially in remote or difficult locations. | Plan for cost efficiency and allocate sufficient resources for unexpected issues. |
| Time Constraints | Completing abandonment in a timely manner while ensuring safety and compliance. | Set realistic timeframes; streamline procedures to avoid unnecessary delays. |
| Subsurface Conditions | Managing complex geological conditions such as high pressure, temperature, and fluid migration. | Use advanced simulation tools to understand subsurface conditions beforehand. |
| Waste Disposal | Ensuring proper disposal or treatment of waste materials from the abandonment process. | Follow best practices for waste management; use approved disposal methods. |
| Monitoring and Reporting | Implementing continuous monitoring systems to ensure well integrity post-abandonment. | Implement robust monitoring systems and periodic reporting for post-abandonment safety. |

How Simulation Technologies are Used for Well Abandonment
Oil and gas simulation technologies play a crucial role in enhancing well abandonment processes by providing a better understanding of the well’s behavior and surrounding environment. These technologies help to optimize the abandonment plan, ensure safety, and mitigate risks.
- Subsurface Modeling and Reservoir Simulation
Advanced reservoir simulation tools are used to create a detailed model of the well’s subsurface environment. These simulations predict how fluids, such as hydrocarbons or water, will behave after the well is abandoned. Understanding the pressure, temperature, and fluid migration in the reservoir allows engineers to identify potential risks such as leakage or fluid contamination before the abandonment process begins.
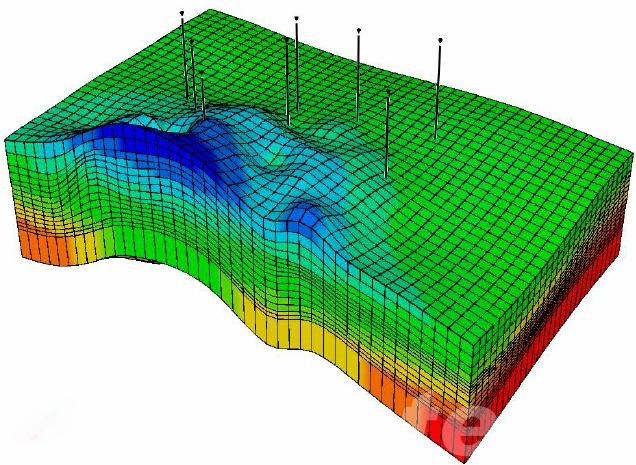
- Well Integrity Analysis
Simulation software can model the mechanical integrity of the wellbore, helping engineers predict the performance of the well’s casing, cement, and barriers over time. This is essential for planning the proper sealing and plugging of the well to prevent fluid migration or contamination. By simulating these conditions, operators can optimize the materials used for sealing and the methods employed to ensure long-term well integrity.
- Plug and Abandonment (P&A) Optimization
Simulation tools help optimize the plug and abandonment process itself. They simulate the placement of cement plugs and the tools used for the job, ensuring the correct sequence of operations. By simulating the entire process, engineers can identify potential challenges, such as tool failure or challenges related to fluid movement, and adjust the abandonment procedures accordingly.

- Pressure and Fluid Migration Simulation
Using fluid flow simulation, engineers can predict how the fluids will behave once the well is shut-in. These simulations help to assess potential risks such as the migration of hydrocarbons or trapped gases. It helps in identifying weak spots in the wellbore and predicting where potential pressure buildup or leakage could occur, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
- Risk Assessment and Contingency Planning
Simulation technologies can assist in conducting risk assessments by simulating worst-case scenarios, such as well failure or unexpected fluid migration. By identifying the most critical risks and providing contingency plans, these technologies help operators prepare for unforeseen challenges during the abandonment process.
- Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental simulations can model the potential impact of well abandonment on surrounding ecosystems. These tools simulate scenarios where residual hydrocarbons or chemicals could leak, helping operators develop strategies to minimize environmental damage. By understanding the potential effects in advance, operators can implement the necessary safety measures.
- Time and Cost Optimization
Simulation technologies help to streamline the abandonment process by optimizing the sequence of operations and resource usage. By simulating different scenarios, operators can identify the most cost-effective approach, reducing unnecessary steps and avoiding delays. This can lead to cost savings and faster execution of the abandonment plan.

Summary
Well abandonment is a vital process in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that wells are safely and permanently sealed at the end of their productive lives. While the process presents challenges, such as high costs and regulatory gaps, addressing these issues is essential to protect the environment, public health, and economic stability. Through following best practices,ensuring compliance with regulations and investing in technological innovations, the oil and gas industry can ensure that well abandonment is carried out effectively, while minimizing risks and maximizing safety.

