How to Address the Regulatory Challenges in Offshore Drilling
Offshore oil drilling is critical in the global energy sector, but it is heavily regulated to ensure environmental protection, worker safety, and operational integrity. Compliance with these regulations is often complex, requiring companies to navigate evolving policies, environmental concerns, and international standards. To successfully address regulatory challenges in offshore drilling, companies must adopt a strategic approach that integrates advanced technologies, proactive compliance management, regulatory engagement, financial planning, etc.

Understanding Offshore Drilling
Offshore drilling is the process of extracting oil and natural gas from beneath the seabed using specialized rigs and platforms. It can enable access to deep-water and ultra-deep-water reserves. This complex operation involves advanced technologies for exploration, well construction, and environmental protection. Due to the high risks associated with offshore drilling, stringent regulations govern safety, environmental impact, and operational efficiency. Innovations in automation, simulation, and digital monitoring continue to improve offshore drilling practices, making them safer and more sustainable.

Regulatory Challenges in Offshore Drilling
This chart highlights the primary regulatory challenges offshore drilling companies face and their impact on operations.
| Regulatory Challenge | Description | Impact on Offshore Drilling |
| Environmental Compliance | Strict regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and spill prevention. | Increased operational costs and the need for advanced monitoring systems. |
| Safety Standards | Requirements for worker safety, blowout prevention, and emergency response. | Mandatory safety training, enhanced equipment regulations, and operational delays. |
| Well Integrity Regulations | Rules ensuring structural stability and pressure control in wells. | Complex well design processes and additional testing requirements. |
| Licensing and Permitting | Lengthy approval processes for exploration and drilling activities. | Delays in project timelines and increased administrative burden. |
| Technology and Equipment Compliance | Regulations governing the use of advanced drilling and monitoring technologies. | Higher investment costs for new equipment and compliance verification. |
| Liability and Insurance Requirements | Financial accountability for accidents, spills, and environmental damage. | Increased insurance costs and legal responsibilities for operators. |
| International Regulatory Variability | Differences in regulations across regions and governing bodies. | Challenges in standardizing operations for global offshore projects. |
| Decommissioning and Abandonment | Regulations on the safe closure of offshore wells and platform decommissioning. | Long-term financial and environmental responsibilities for companies. |

Strategic Approaches to Address the Regulatory Challenges in Offshore Drilling
1. Leveraging Technology for Compliance
Advanced technology plays a crucial role in meeting regulatory requirements and improving operational efficiency. Real-time monitoring systems, automated shutoff mechanisms, and AI-driven predictive maintenance help companies detect potential issues before they escalate into regulatory violations. Remote-operated vehicles (ROVs) and drones are also increasingly used for underwater inspections, reducing the need for human divers and enhancing safety compliance.
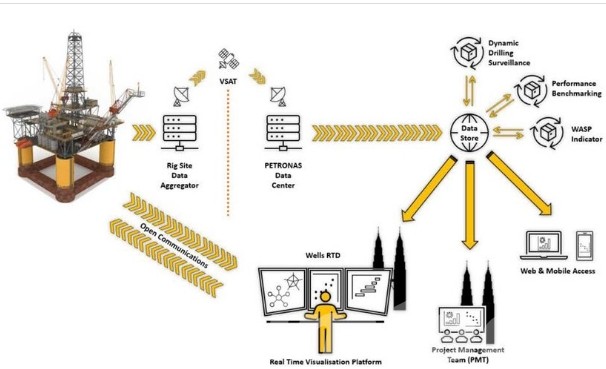
In addition, environmentally friendly drilling technologies, such as carbon capture systems and low-emission fuel alternatives, are essential for adhering to strict environmental regulations. Innovations like managed pressure drilling (MPD) and blowout preventers (BOPs) enhance well control, reducing the risk of oil spills and environmental disasters. By investing in such technologies, offshore drilling operators can not only improve compliance but also optimize operational costs.
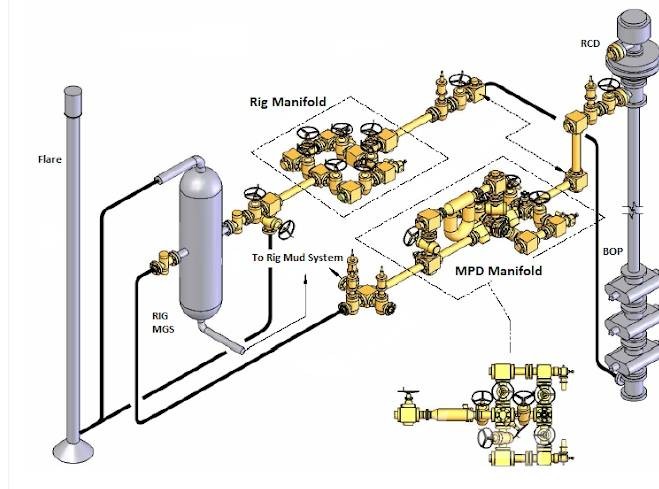
2. Implementing Strong Risk Management and Compliance Frameworks
Proactive risk management is key to addressing regulatory challenges in offshore drilling. Companies must conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments (EIAs) before initiating any drilling operations to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. Regular audits, safety drills, and compliance training programs ensure that workers and management teams remain updated on the latest regulatory requirements.
Implementing globally recognized safety management systems, such as those set by the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE) or the International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC), helps companies align with international best practices. A strong internal regulatory compliance team is also essential for tracking policy changes and adapting company protocols accordingly.
3. Engaging with Regulatory Bodies and Stakeholders
Regulatory compliance is not just about following rules—it is also about maintaining open communication with governing bodies and stakeholders. Offshore drilling companies should actively engage with regulatory agencies, environmental groups, and local communities to address concerns and contribute to policy development. By participating in regulatory discussions, companies can gain valuable insights into upcoming legislative changes and prepare accordingly.
Transparency in reporting is another essential aspect of regulatory engagement. Regular disclosures of safety records, environmental impact data, and corporate responsibility initiatives build trust with regulators and the public. Public perception can influence regulatory decisions, making it important for drilling companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible drilling practices.
4. Harmonizing International Regulations
One of the biggest challenges in offshore drilling is the variation in regulations across different jurisdictions. Companies operating in multiple regions must comply with a range of regulatory frameworks, which can create inconsistencies and increase operational costs. Efforts to standardize regulations through international bodies such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Regulators’ Forum (IRF) can help streamline compliance requirements.
Industry-wide collaborations and partnerships can also promote best practices and reduce discrepancies between regional regulations. Working together with global regulators ensures that companies can operate more efficiently while maintaining high safety and environmental standards.
5. Managing Financial Costs of Compliance
Regulatory compliance often comes with significant financial burdens, including the cost of new technologies, operational adjustments, and environmental safeguards. To address these challenges, companies can seek government incentives and tax benefits for implementing sustainable drilling practices. Investing in research and development (R&D) for cleaner energy solutions can also position companies for long-term regulatory compliance while improving operational efficiency.
Additionally, adopting cost-effective risk management strategies—such as predictive maintenance to prevent equipment failures—can help reduce fines and penalties associated with non-compliance. By proactively integrating compliance measures into business operations, offshore drilling firms can avoid costly disruptions while maintaining regulatory adherence.

How Simulation Technologies Are Used for Addressing the Regulatory Challenges in Offshore Drilling
Oil and gas simulation technologies have emerged as powerful tools to help offshore operators meet regulatory demands by enhancing safety training, optimizing drilling performance, and improving environmental compliance.

- Enhancing Safety and Compliance Training
One of the key regulatory challenges in offshore drilling is ensuring that personnel are well-trained to handle emergencies, operate equipment safely, and comply with safety standards. Simulation-based training provides a realistic and immersive learning environment that allows workers to practice complex procedures without real-world risks.
Advanced drilling simulators replicate offshore conditions, enabling personnel to experience blowout prevention, well control, and emergency shutdown procedures. These simulations help companies meet safety regulations set by organizations such as the International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC) and the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE) by ensuring that workers are well-prepared for real-life scenarios.

- Optimizing Drilling Operations for Regulatory Compliance
Regulations often require offshore operators to minimize operational risks, optimize well construction, and reduce non-productive time. Simulation technologies enable companies to model various drilling scenarios before actual execution, helping them make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and safety.
- Well Planning and Design: Well control simulation system helps engineers analyze different drilling parameters to ensure regulatory compliance regarding well integrity and structural safety.
- Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD) Simulations: MPD is a technique used to precisely control wellbore pressure and reduce the risk of well control incidents. Simulation models assist in determining optimal pressure management strategies to meet regulatory requirements.
- Equipment Performance Testing: Simulations allow operators to test and optimize the performance of critical drilling equipment, such as blowout preventers and mud circulation systems, ensuring they function within required safety margins.
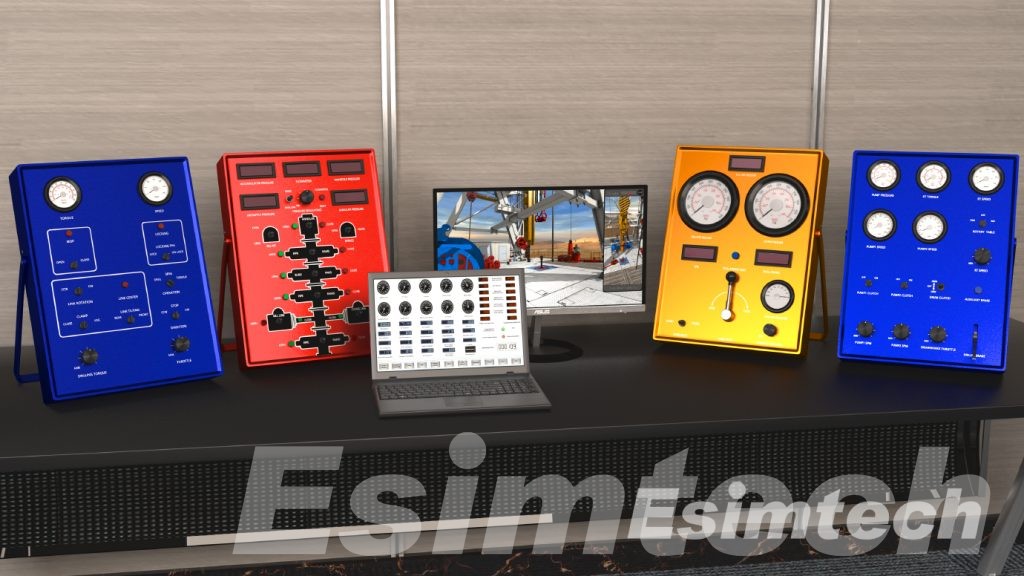

- Supporting Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations in offshore drilling focus on preventing oil spills, reducing carbon emissions, and minimizing the impact on marine ecosystems. Simulation technologies aid in achieving compliance by:
- Spill Response Simulation: Virtual modeling of oil spill scenarios helps operators develop and test emergency response plans in compliance with international environmental regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Digital twin simulations allow companies to assess and optimize fuel consumption, rig emissions, and energy efficiency, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Marine Impact Assessment: Simulations of ocean currents and ecosystem interactions help drilling companies predict the potential impact of their operations on marine biodiversity, ensuring adherence to environmental protection guidelines.
- Improving Regulatory Audits and Compliance Verification
Simulation technologies also play a vital role in regulatory reporting and audit preparation. Digital models enable companies to track and document operational data in real time, making it easier to demonstrate compliance during inspections. Virtual reality emergency simulations of past incidents help regulatory bodies assess risk mitigation strategies and improve safety standards across the industry.

Wrap Up
Addressing regulatory challenges in offshore drilling requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technological advancements, proactive risk management, regulatory engagement, international standardization, and financial planning. Through integrating simulation-based training, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring, oil and gas drilling companies can enhance regulatory adherence while improving overall operational effectiveness.

