Horizontal Oil Drilling: What is it and Why Simulation Technology is Important for it
Horizontal oil drilling, a groundbreaking innovation in the oil and gas industry, has transformed how hydrocarbon resources are accessible and produced. Vertical drilling was once the standard, but horizontal drilling has opened up new opportunities by allowing operators to access previously inaccessible reserves. In this article, we will explore the process, advantages, challenges, environmental considerations, and vital role of simulation technology associated with horizontal oil drilling.

Process of Horizontal Oil Drilling
Horizontal drilling, also known as directional drilling, is the process of drilling a wellbore at an angle in order to get access to oil or gas reservoirs beneath the Earth’s surface. Horizontal drilling, as opposed to vertical drilling, oil drilling both vertically and horizontally. The procedure can be summed up as follows:
1. Vertical Drilling
A wellbore is initially drilled vertically from the surface to a certain depth.
2. Build Section
At a specific depth, the drilling direction is changed, and the wellbore is curved to create a “build section”
3. Horizontal Drilling
After the curve, the wellbore continues horizontally through the oil or gas reservoir.

4. Well Completion
Once the desired length of the horizontal section is achieved, the well is completed with casing and cement to allow for production.
Advantages of Horizontal Oil Drilling
Increased Reservoir Access
Horizontal drilling enables operators to access reservoirs that would otherwise be unreachable via typical vertical drilling. This increases the amount of oil and gas that can be recovered.
Enhanced Recovery Rates
A well’s horizontal portion provides for more contact with the reservoir, resulting in higher recovery rates.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Operators can reduce surface footprint and environmental damage by accessing reservoirs from a single drilling location.
Improved Well Economics
Horizontal drilling is commercially appealing due to higher recovery rates and lower drilling costs.
Enhanced Well Control
Controlling the trajectory of a well allows operators to avoid geological complications and potential drilling issues.
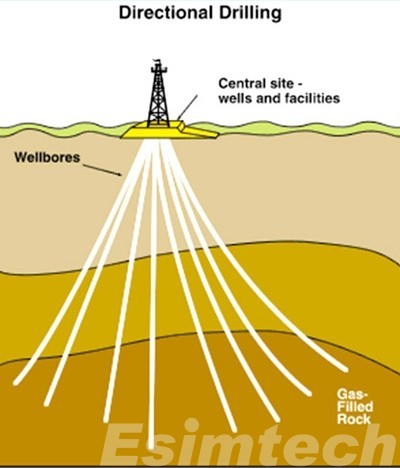
Challenges and Environmental Considerations Faced by Horizontal Oil Drilling
While horizontal drilling offers numerous advantages, it also presents unique challenges and considerations.
Challenges
Technical Complexity: Horizontal drilling is more technically difficult than vertical drilling, necessitating sophisticated equipment and skill.
Increased Costs: Horizontal drilling technology and skill can result in higher initial expenses.
Regulatory Compliance: Operators must adhere to strict regulations to ensure safe and environmentally responsible drilling.
Wellbore Integrity: Maintaining wellbore integrity is critical to prevent accidents and ensure the well’s long-term productivity.

Environmental Considerations
Horizontal drilling has brought several environmental considerations to the forefront:
Reduced Surface Impact: Horizontal drilling minimizes surface disruption, which is especially beneficial in ecologically sensitive areas.
Risk of Contamination: The potential for groundwater contamination from drilling fluids and hydrocarbon migration must be carefully managed.
Spill Prevention: Comprehensive spill prevention and response plans are essential to address potential environmental risks.
Habitat Protection: Operators must consider the impact on local wildlife habitats and ecosystems.
Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to environmental regulations and best practices is essential to mitigate the environmental impact.
Important Role of Simulation Technology in Horizontal Oil Drilling
The use of simulation in the design and execution of horizontal drilling projects is critical. It gives engineers and drillers the knowledge and tools they need to make informed decisions and improve the drilling process.
Geosteering
Geologists and geosteerers can use simulation software to construct 3D models of the subsurface, allowing them to see rock forms and potential obstructions. Geosteerers can precisely guide the drill bit within the reservoir by continuously updating the model in real time using data from downhole sensors.
Drilling Trajectory Planning
Drilling and well simulation system aids in the design of the ideal well path by taking geological data, wellbore stability, and reservoir parameters into account. It enables engineers to plot the most efficient path, minimizing the chances of getting trapped or veering off course.

Wellbore Stability Analysis
Oil simulation software can predict the mechanical behavior of the wellbore and drill string. It evaluates the strains and pressures operating on the wellbore walls and forecasts the likelihood of issues such as wellbore collapse or fluid ingress. This data informs the selection of drilling parameters as well as the design of the drilling assembly.
Real-time Monitoring and Adjustments
During drilling process, data from downhole sensors and measurements are fed into the simulation software. This real-time feedback allows drillers to make immediate adjustments to the drilling parameters, ensuring the drill bit remains within the target zone.

Benefits of Simulation in Horizontal Drilling
Precision and Accuracy: Simulation provides a high level of precision in wellbore placement. It helps minimize deviation from the target zone, ensuring that the well intercepts the most productive areas of the reservoir.
Enhanced Efficiency: By optimizing wellbore trajectories and drilling parameters, simulation reduces drilling time and operational costs. It also minimizes the risk of complications that can lead to costly delays.
Risk Mitigation: Simulation helps in identifying potential drilling challenges in advance, allowing for proactive risk management and wellbore stability assurance.
Improved Recovery Rates: Accurate well placement in the reservoir maximizes hydrocarbon recovery, leading to higher production rates and increased profitability.
Safety and Environmental Protection: Simulation helps prevent issues like wellbore instability, fluid influx, or well collisions, which can pose safety risks and environmental concerns.

Conclusion
Horizontal oil drilling has revolutionized the oil and gas industry by allowing access to previously undiscovered sources and increasing recovery rates. Oil and gas simulation guarantees that horizontal drilling operations are optimized for optimum hydrocarbon recovery by properly simulating well trajectories, analyzing wellbore stability, and giving real-time guidance. Horizontal drilling will play a critical part in assuring a sustainable and efficient future for the oil and gas sector, satisfying the world’s energy demands while safeguarding the environment, as technology and industry practices continue to evolve.

