Geological Modeling for Oil and Gas Exploration: Techniques and Application
Geological modeling is an essential process in the exploration and production of oil and gas resources. It helps geologists and engineers understand the subsurface formations and predict the behavior of reservoirs. By creating a virtual representation of the subsurface, geological modeling enables the efficient and safe extraction of hydrocarbons. This article covers the basics of geological modeling, the importance of 3D models, and its various applications in oil and gas exploration.
Basics of Geological Modeling in Oil and Gas
Geological modeling in oil and gas exploration provides the basis for informed decision making throughout the reservoir lifecycle. It involves constructing digital models of the subsurface geology that allow geologists and engineers to visualize the distribution of rock formations, fluid reservoirs, and structural features. These models are important for assessing the size, properties, and behavior of oil and gas fields, ultimately helping to develop more precise exploration, drilling, and production strategies.
What is Geological Modeling?
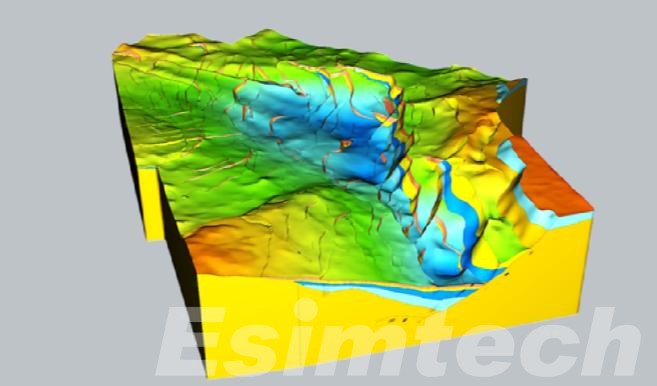
Geological modeling in oil and gas involves creating a detailed, digital representation of the Earth’s subsurface to better understand and visualize the geological properties of reservoirs. This process combines various data sources, including seismic surveys, well logs, core samples, and outcrop studies, to generate a comprehensive model of the subsurface environment. These models can be either 2D or 3D, with 3D models offering more precise insights into the spatial arrangement of geological features.
The main objective of geological modeling is to predict the behavior of oil, gas, and water within a reservoir. By simulating fluid dynamics and rock properties, geologists can assess the potential for hydrocarbon accumulation and evaluate the project’s economic viability. Additionally, geological models provide a framework for risk assessment, enabling operators to test different extraction scenarios and predict future reservoir behavior under various conditions.
Key Components of Geological Modeling
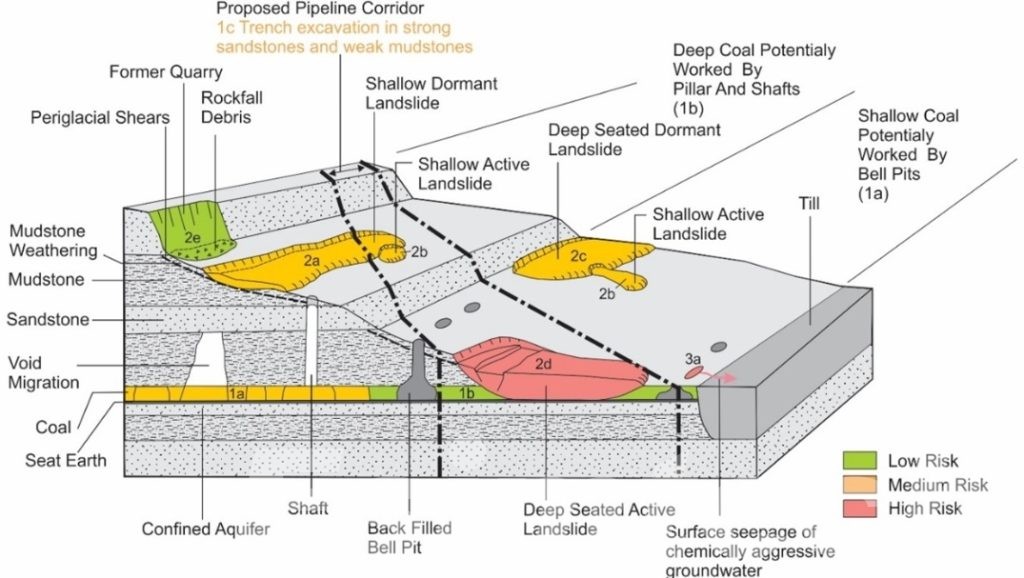
Geological modeling involves several key components that work together to create an accurate representation of the subsurface:
- Data Collection: The process begins with gathering diverse geological data from sources such as seismic surveys, well logs, core samples, and outcrop studies. Seismic data helps map large-scale subsurface structures, while well logs and core samples provide detailed, localized information about rock and fluid properties.
- Data Integration: Collected datasets are combined into a unified framework using advanced software tools. This process ensures that seismic data, well logs, and geological maps are accurately aligned, resulting in a cohesive model that represents the true nature of the subsurface.
- Stratigraphy and Structural Analysis: Stratigraphy examines the layering and continuity of rock formations, while structural analysis focuses on identifying faults, folds, and other geological features that impact fluid flow and the geometry of the reservoir.
- Reservoir Characterization: Key reservoir properties, such as porosity, permeability, and fluid saturation, are assessed. These parameters are crucial for predicting fluid storage and flow capabilities within the reservoir.
- Visualization: The completed model is displayed in 2D or 3D, offering a clear depiction of subsurface geology. These visual representations aid decision-making by helping geologists and engineers pinpoint optimal drilling sites and enhance resource extraction strategies.
These components combine to create reliable models, reducing uncertainties and improving exploration and production outcomes.
Static vs. Dynamic Geological Modeling
Geological modeling is categorized into static and dynamic models, each serving distinct purposes in understanding reservoirs.
- Static Geological Modeling provides a time-independent representation of the subsurface, focusing on the physical and structural properties of the reservoir. These models detail rock types, porosity, permeability, and geological structures, offering a snapshot of the reservoir’s characteristics. Static models are vital during exploration and early field development, helping to estimate reserves, define reservoir boundaries, and guide drilling plans.
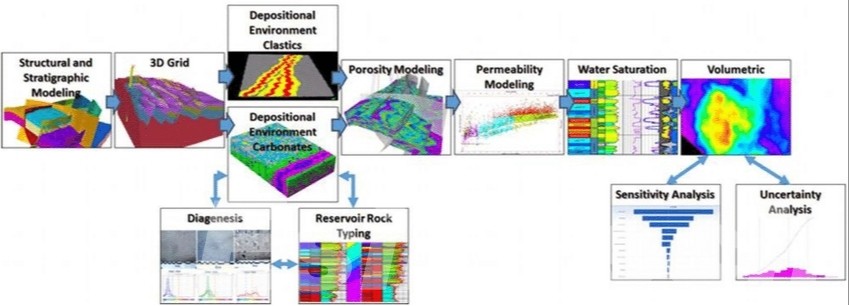
- Dynamic Geological Modeling, on the other hand, incorporates changes over time by simulating fluid flow, pressure variations, and production dynamics within the reservoir. These models predict reservoir behavior under different extraction scenarios, optimizing production strategies and enhancing recovery techniques such as water flooding or gas injection.

By combining both models, operators gain a comprehensive understanding of the reservoir, from its geological framework to its performance over time, enabling more informed decision-making and efficient resource management.
Benefits of 3D Geological Modeling in Oil and Gas
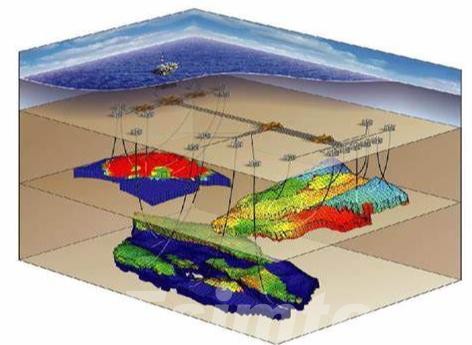
Three-dimensional geological modeling has become a transformative tool in the oil and gas industry, offering a deeper understanding of complex subsurface environments. Its advanced capabilities bring numerous benefits to exploration and production activities:
- Increased Accuracy and Detail: 3D models provide a highly precise and detailed representation of the subsurface, reducing uncertainties and improving interpretations of geological features like faults, fractures, and stratigraphic layers. This accuracy enhances drilling success rates and resource estimation.
- Enhanced Visualization: These models offer an intuitive, immersive view of the subsurface, allowing geologists and engineers to explore reservoir structures in greater depth. This visual clarity aids in understanding geological complexities and fluid distribution patterns.
- Optimized Resource Management: By pinpointing productive zones and reservoir boundaries, 3D models help identify optimal drilling locations, plan effective extraction strategies, and minimize resource wastage.
- Risk Reduction: Through the simulation of various scenarios, such as fluid flow and pressure changes, 3D models help assess operational risks. This foresight reduces the likelihood of costly errors, such as drilling dry wells or encountering unforeseen subsurface challenges.
- Adaptability to Complex Reservoirs: Modern oil and gas exploration often targets challenging environments, such as deepwater or unconventional resources. 3D modeling excels in such contexts by visualizing intricate geological structures and fluid behaviors with remarkable precision.
Overall, 3D geological modeling enhances the efficiency, safety, and profitability of oil and gas operations. By combining accuracy, visualization, and predictive capabilities, it enables operators to tackle industry challenges with greater confidence.
Application of Geological Modeling in Oil and Gas
Geological modeling plays a vital role across all stages of the oil and gas industry, enabling better decision-making and operational efficiency. Below are its key applications:
- Oil and gas reservoir evaluation: Geological modeling can help evaluate the reserves, quality and mining difficulty of oil and gas reservoirs, and provide a basis for oil and gas field development decisions. Through geological modeling, the distribution and reserves of oil and gas reservoirs can be predicted more accurately, thereby optimizing the development plan of oil and gas fields.
- Oil and gas reservoir modeling: Geological modeling provides basic data for oil and gas reservoir modeling, which is used to simulate reservoir fluid flow, predict oil and gas recovery rate and formulate development plans. Through geological modeling, we can have a deeper understanding of the geological characteristics and fluid flow laws of oil and gas reservoirs, thereby improving oil and gas recovery rate.
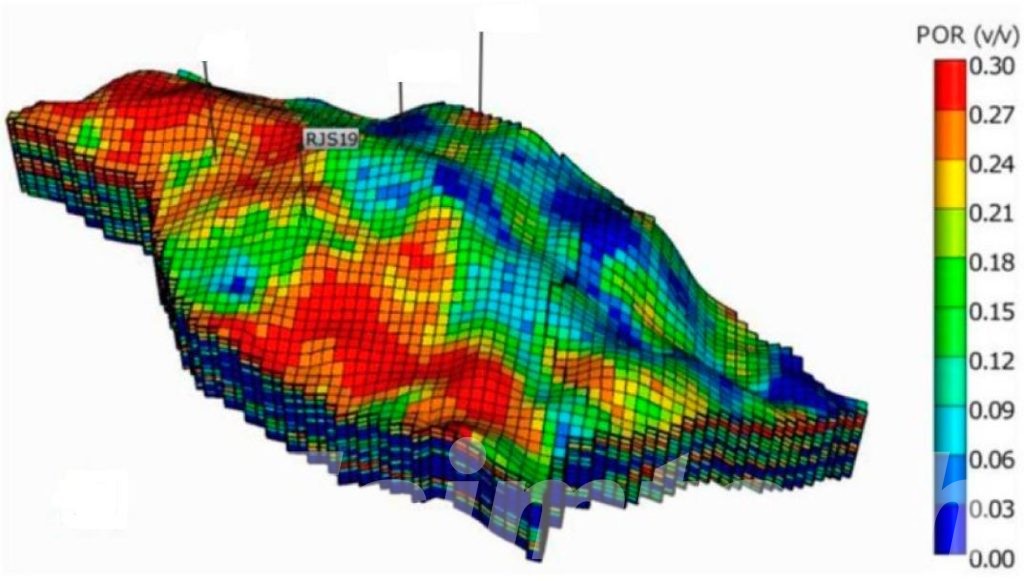
- Oil and gas development optimization: Geological modeling can optimize well layout, injection and production plans and development methods, and improve oil and gas development efficiency and benefits. Through geological modeling, the dynamic changes of oil and gas reservoirs can be more accurately predicted, thereby optimizing the development strategy of oil and gas fields.
- Oil and gas resource evaluation: Geological modeling can provide basic data for oil and gas resource evaluation, which is used to predict the potential and distribution law of oil and gas resources in a certain area. Through geological modeling, the distribution and reserves of oil and gas resources can be more accurately evaluated, thereby providing a scientific basis for the development and management of oil and gas resources.
- Digital modeling of oil and gas reservoirs: Geological modeling technology is the basis of digital modeling of oil and gas reservoirs, which aims to reconstruct the geological structure and properties of reservoirs and provide support for subsequent development decisions. Through geological modeling, the geological characteristics and properties of oil and gas reservoirs can be described more accurately, thus providing a scientific basis for the development and management of oil and gas fields.
Geological modeling is essential in oil and gas exploration, providing detailed subsurface insights for efficient resource discovery and management. Advancements in 3D modeling have improved accuracy, visualization, and cost efficiency, reducing risks and optimizing operations. Spanning exploration to decommissioning, geological modeling drives innovation and supports sustainable practices, cementing its role as a cornerstone of the industry.
