Exploring the Innovative Technologies for Well Intervention Operations
Well intervention operations in the oil and gas sector have traditionally used conventional methods like as wireline, coiled tubing, and hydraulic workover units. However, with the advent of innovative technologies, the landscape of well intervention has experienced a significant upheaval. In this article, we explore some of the advanced technologies revolutionizing well intervention opeations and their impact on the industry.

Understanding the Basics of Well Intervention
In the oil and gas industry, well intervention operations are essential for maintaining and optimizing production from oil and gas wells.
| Aspects | Description |
| Definition | Well intervention refers to activities conducted on oil or gas wells to increase or restore production, improve well integrity, or perform maintenance and repair tasks. |
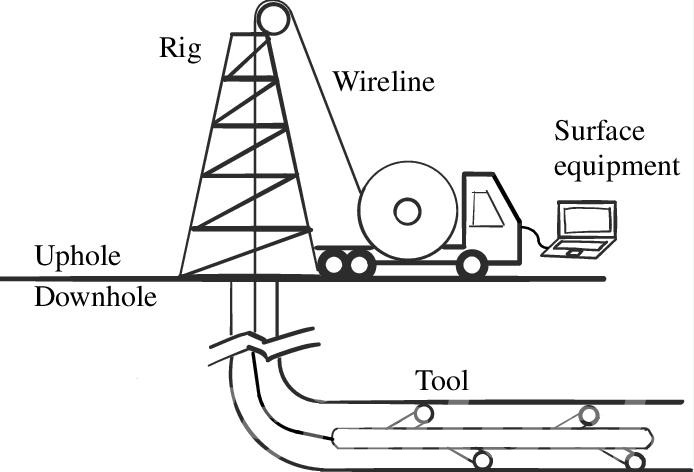
| Types of Well Intervention | Wireline Intervention: Uses a cable to deploy tools and equipment into the wellbore for services such as logging, perforating, or setting plugs and packers. Coiled Tubing Intervention: Involves injecting a continuous length of tubing into the well to perform services like cleanouts, milling, or acidizing. Snubbing Intervention: Utilizes a hydraulic unit to insert and extract pipe strings under pressure, enabling operations in live wells without shutting in production. Hydraulic Workover (HWO): Involves rigging up a workover rig to perform more extensive interventions like completions, sidetracking, or wellbore remediation. |
| Benefits | Increase Production: Stimulate reservoirs, remove obstructions, or repair damaged equipment to enhance production rates. Enhance Well Integrity: Address integrity issues, isolate zones, or plug and abandon wells to prevent environmental contamination or wellbore instability. Perform Maintenance: Conduct routine maintenance tasks, such as cleaning, tubing replacements, or equipment inspections, to ensure optimal well performance. Improve Reservoir Management: Gather data through logging or testing, install monitoring equipment, or implement reservoir stimulation techniques for enhanced recovery. |
Advanced Technologies in the Well Intervention Operations
1. Advanced Robotics
- Robotic systems with sensors and actuators provide precise and autonomous intervention in wellbores.
- These robots can explore complicated downhole settings, perform diagnostics, and repairs with high accuracy.
- Advanced robotics improve good intervention operations by eliminating human intervention and operational risks, increasing safety and efficiency.
2. Intelligent Downhole Tools
- Intelligent downhole tools incorporate sensors and control systems to monitor downhole conditions and optimize well performance.
- Smart tools, such as intelligent well tractors and autonomous inflow control devices, enable real-time adjustments to flow rates and production profiles.
- By enhancing reservoir management and production optimization, intelligent downhole tools maximize recovery rates and asset profitability.
3. Fiber Optic Sensing and Monitoring
- Fiber optic sensing technology enables precise monitoring of downhole conditions such as temperature, pressure, and fluid flow.
- Distributed temperature sensing (DTS) and distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) provide real-time information on reservoir dynamics and wellbore integrity.
- Precise reservoir data enables operators to improve production methods, identify possible concerns, and make educated decisions during well interventions.

4. Nanotechnology and Microscale Intervention
- Nanoparticles, micro-robots, and microfluidic devices allow for precise manipulations at the nano and microscale levels within wellbores.
- These small tools provide fine control over fluid flow, chemical reactions, and mechanical interventions, improving reservoir stimulation and recovery.
- Nanotechnology and microscale intervention technologies improve productivity in tough situations by opening up new reservoir engineering opportunities.
5. Electromagnetic Heating and Thermal Technologies
- Electromagnetic heating systems, such as radiofrequency (RF) and microwave technologies, provide targeted heating of reservoirs to improve fluid mobility and enhance oil recovery.
- Thermal methods, including steam injection and in-situ combustion, stimulate reservoirs and optimize production in heavy oil and unconventional reservoirs.
- By leveraging advanced heating and thermal technologies, operators can unlock previously untapped reserves and maximize asset profitability.
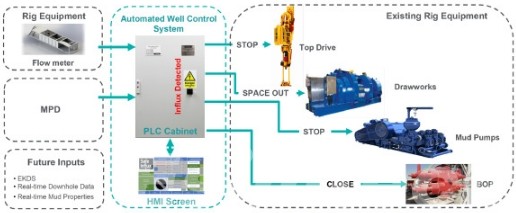
6. Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
- Advanced analytics platforms utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to analyze downhole data and optimize intervention strategies.
- Predictive maintenance models anticipate equipment failures, optimize intervention schedules, and minimize downtime in well operations.
- By harnessing the power of data analytics, operators can improve operational efficiency, extend equipment lifespan, and enhance overall well performance.
Simulation Technology Used in Innovating Well Intervention
1. Reservoir Simulation
- Reservoir simulation software models the behavior of underground reservoirs, includingfluid flow, pressure distribution, and production performance.
- By simulating different well intervention scenarios, operators can optimize production strategies, identify potential issues, and maximize hydrocarbon recovery.
- Reservoir simulation allows operators to forecast reservoir behavior, plan intervention activities, and evaluate the effectiveness of various interventions before implementation.
2. Wellbore Modeling
- Wellbore simulation tools model the geometry, trajectory, and integrity of wellbores, including casing, tubing, and completion components.
- By simulating wellbore conditions and interactions with reservoir fluids, operators can assess the feasibility of interventions, such as perforation, logging, and stimulation treatments.
- Wellbore modeling enables operators to identify potential risks, optimize intervention designs, and ensure the integrity and efficiency of intervention operations.

3. Hydraulic Fracturing Simulation
- Hydraulic fracturing simulation software simulates the spread of hydraulic fractures in reservoir formations during stimulation treatments.
- By simulating fracture networks, fluid flow patterns, and proppant placement, operators can improve fracturing designs, increase reservoir connectedness, and increase production rates.
- Hydraulic fracturing simulator allows operators to assess various fracturing situations, reduce risks, and optimize fracture treatments to improve well performance.

4. Coiled Tubing and Wireline Simulation
- Coiled tubing and wireline simulation tools model the deployment and operation of intervention equipment in wellbores, including tubing, tools, and fluids.
- By simulating downhole conditions, tool behavior, and operational parameters, operators can plan and execute interventions with precision, efficiency, and safety.
- Coiled tubing and wireline simulation enable operators to optimize job designs, assess wellbore conditions, and minimize the risk of equipment failures or stuck tools during interventions.

5. Real-Time Monitoring and Control Simulation
- Real-time monitoring and control simulation systems mimic the behavior of downhole sensors, control systems, and surface equipment during intervention operations.
- Simulating data gathering, processing, and decision-making processes allows operators to evaluate monitoring system performance, analyze data trends, and optimize control methods in real time.
- Real-time monitoring and control simulation improve situational awareness, allow for proactive interventions, and increase operational efficiency during well intervention activities.

Conclusion
Innovative technologies are driving transformative changes in well intervention operations, enabling operators to unlock new reserves, optimize production efficiency, and maximize asset profitability. Simulation technology plays a vital role in driving innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in well intervention operations. Embracing these innovative solutions will be essential for staying competitive and sustainable in a rapidly changing energy landscape.