Exploring Oil Drilling Rigs: Types, Functions and Innovations
Oil drilling rigs provide crucial infrastructure for discovering and producing hydrocarbons deep beneath the Earth’s surface. These tall structures, which are frequently positioned both onshore and offshore, are engineering and technological marvels. This article will go into the world of oil drilling rigs, analyzing their various types, functions, and innovations that have transformed the industry.

What are the Common Types of Oil Drilling Rigs
Onshore Rigs
Conventional Land Rigs: These are the most often utilized onshore drilling rigs for drilling vertical and deviated wells. Traditional land rigs are adaptable and can be used in a variety of geological environments.
Mobile Drilling Units: These are portable drilling rigs that are designed for quick setup and dismantling. They are frequently employed for exploratory drilling and are highly movable, enabling for easy relocation.
Offshore Rigs

Jack-Up Rigs: Jack-up rigs are transportable offshore platforms that have extensible legs and may be lowered to the seafloor. Once the legs are in place, the rig is “jacked up” above the water’s surface to provide stability while drilling. In shallow waters, these rigs are often utilized.
Semi-Submersible Rigs: Semi-submersible rigs are buoyant pontoons and columns that float. They partially submerge, offering exceptional stability even in rough seas. Semi-submersibles are employed in deep and ultra-deep waters for exploration and production.
Drillship Rigs: Drillships are self-propelled vessels equipped for drilling operations. Drill ship rigs have dynamic positioning systems that allow them to remain stationary over drilling sites without anchors. Drillships are highly mobile and operate in deepwater and remote locations.

Tension Leg Platforms (TLPs): TLPs are floating platforms tethered to the seabed with vertical tendons. The floating oil rigs provide stability while allowing vertical movement due to wave action. TLPs are suitable for deepwater drilling and production.

What are the Functions of Oil Drilling Rigs
Exploration Drilling
Site Assessment: In any exploration project, the initial role of an oil drilling rig is site appraisal. Geologists and engineers use geological data and seismic studies to locate prospective drilling areas. Once a suitable area has been identified, the drilling rig is transported to that location.
Wildcat Wells: Exploratory drilling, often referred to as wildcat drilling, involves drilling test wells to evaluate the presence and potential quantity of hydrocarbons beneath the Earth’s surface. These initial wells are crucial for identifying prospective reserves.
Production Drilling
Production Wells: Once promising reserves are confirmed through exploration, drilling rigs are used to create production wells. These wells serve as conduits for bringing oil and gas to the surface. Production drilling is the primary function of drilling rigs, allowing for the extraction of hydrocarbons.
Appraisal Drilling
Reserve Evaluation: Appraisal drilling comes after initial discoveries to assess the size and quality of the hydrocarbon reserves. Multiple appraisal wells are drilled to gather data on the reservoir’s characteristics, such as pressure, temperature, and hydrocarbon composition. This information aids in determining the commercial viability of the reserves.
Optimizing Production: Appraisal drilling assists operators in determining the most efficient method of extracting hydrocarbons from a reservoir while maximizing recovery rates.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Drilling
Secondary Recovery: Some drilling rigs are specifically designed to use enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques. EOR involves injecting fluids, gases, or chemicals into the reservoir to increase hydrocarbon extraction rates. This drilling function is aimed at maximizing production from mature oil fields.
Directional and Horizontal Drilling
Accessing Remote Reserves: Directional and horizontal drilling is used when hydrocarbon reserves are not directly beneath the drilling location. These drilling techniques enable operators to access reservoirs located far from the initial drilling point, improving reservoir access and recovery.
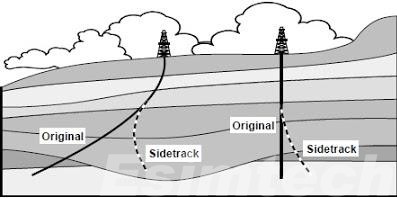
Well Maintenance and Workovers
Wellbore Integrity: Drilling rigs are used to drill producing wells after potential reserves have been identified through exploration. These wells serve as passageways for oil and gas to the surface. The primary function of drilling rigs is to extract hydrocarbons through production drilling.
Plug and Abandonment (P&A)
Retiring Wells: Drilling rigs are utilized for plug and abandonment operations when a well reaches the end of its productive life or is no longer economically viable. This procedure entails sealing the wellbore to avoid leakage or contamination of the environment. Proper well abandonment is a crucial aspect of responsible drilling.

What are the Noteworthy Innovations in Oil Drilling Rigs
Automation and Remote Monitoring
Automation has revolutionized drilling operations by enhancing precision and reducing human error. Advanced control systems and sensors are now commonly integrated into drilling rigs, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis. This data can be transmitted to remote control centers, where experts can monitor operations and make critical decisions in real-time. Automation not only improves drilling accuracy but also enhances safety by reducing the need for human intervention in high-risk situations.
Top Drives
Top drives are motorized drilling systems installed on the derrick or mast of drilling rigs. They provide rotational power to the drill string, enabling faster and more controlled drilling. Top drives are versatile and can handle complex drilling tasks, including directional drilling and extended-reach drilling. Their efficiency and precision make them essential components in modern drilling operations, increasing overall rig productivity.
The top drive simulation training system has been developed with the goal of training the functioning of the top drive device. It may provide training for all top drive operations as well as common accident handling. It can be utilized for driller/driller assistant, technician, and drilling team leader training. Trainees can master the operating method of top drive and the handling skills of common mishaps by training with the system.
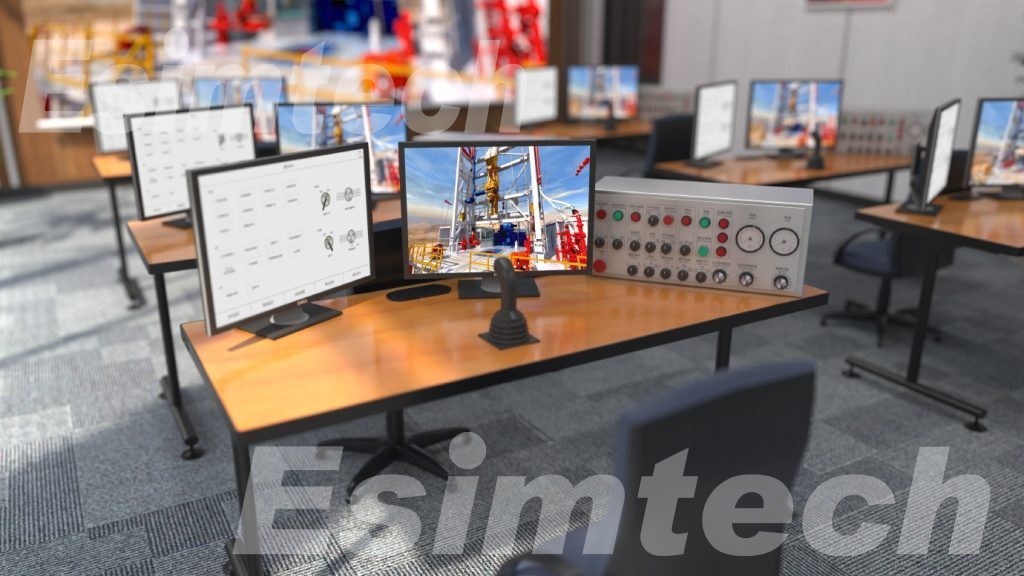

The system employs numerous mathematical models to simulate the operation of the top drive, taking into account the changing rules of various factors. Event-driven simulation technology may model diverse device operations, bringing training closer to reality. Accidents pre-set technology simulates common accidents and gadget flaws, allowing the instructor to enter the accidents or flaws at any moment. The trainee can then judge the phenomenon and take appropriate action. This enhances their ability to judge and handle accidents. Virtual reality technology creates a perceptual environment; 3D animation that is synchronized with operation displays the site scene, together with a rich sound effect. All of this contributes to an immersive training experience.
Directional Drilling Technologies
In the oil and gas industry, directional drilling is becoming increasingly significant. It enables operators to gain access to reservoirs that are not directly beneath the drilling site. Innovations in directional drilling technologies, such as rotary steerable systems and measurement-while-drilling (MWD) equipment, have allowed for more accurate drilling of deviated and horizontal wells. This not only increases reservoir recovery but also decreases environmental impact by reducing the number of drilling locations.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology creates virtual models of drilling rigs, replicating their physical counterparts in the digital realm. These digital twins simulate and optimize drilling processes, allowing operators to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before they occur in the real world. The drilling simulation system adopting digital twins, enhances safety, minimizing downtime, and maximizing drilling efficiency.

Dual Gradient Drilling
Dual gradient drilling (DGD) systems are a revolutionary technique for offshore drilling. These systems control the density of drilling fluids using unique fluid management techniques, allowing them to maintain consistent well pressure even in deepwater and high-pressure situations. DGD not only improves drilling safety but also reduces the risk of blowouts and environmental incidents.
Enhanced Drilling Fluids
The advancement of improved drilling fluids has resulted in more efficient and environmentally friendly drilling operations. Water-based muds and synthetic-based fluids are environmentally friendly drilling fluids that are designed to lessen environmental impact while preserving drilling performance. They increase lubrication, temperature stability, and wellbore stability, making drilling safer and more sustainable.
Wellbore Monitoring and Control Systems
Advanced wellbore monitoring and control systems are standard on modern drilling rigs. These devices assess downhole conditions, detect anomalies, and improve drilling parameters using real-time data. They improve drilling accuracy and safety by continuously monitoring and warning of potential concerns including kicks and wellbore instability.
Conclusion
Oil drilling rigs are the industry’s backbone, allowing for the exploration and production of essential hydrocarbon resources. These oil rigs range from onshore to offshore and perform a variety of roles. Recent technical advancements have made drilling operations safer, more efficient, and less harmful to the environment. Oil drilling rigs are at the vanguard of innovation in the energy business, unlocking new reserves and assuring a sustainable energy future.

